Electromagnet and concept of Electromagnetism is a fascinating topic in Physics that combines electricity and magnetism, leading to the creation of electromagnets, which are essential in various applications. Let’s delve into the key aspects related to electromagnets:
supremetutorials

Historical background of Electromagnet & Electromagnetism – Electromagnet and concept of Electromagnetism
The study of electromagnetism dates back to ancient times when people observed the natural occurrence of magnetic phenomena. However, it was not until the 19th century that significant advancements were made, thanks to the pioneering work of scientists like Michael Faraday and James Clerk Maxwell.
1. Definition of Electromagnet
1. Definition: An electromagnet is a type of magnet that generates a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. Unlike permanent magnets, electromagnets can be turned on and off, making them highly versatile.
At its core, electromagnetism refers to the interaction between electric charges and magnetic fields. It is governed by a set of fundamental laws and principles that describe the behavior of electromagnetic forces.
Principles of Electromagnetic Induction
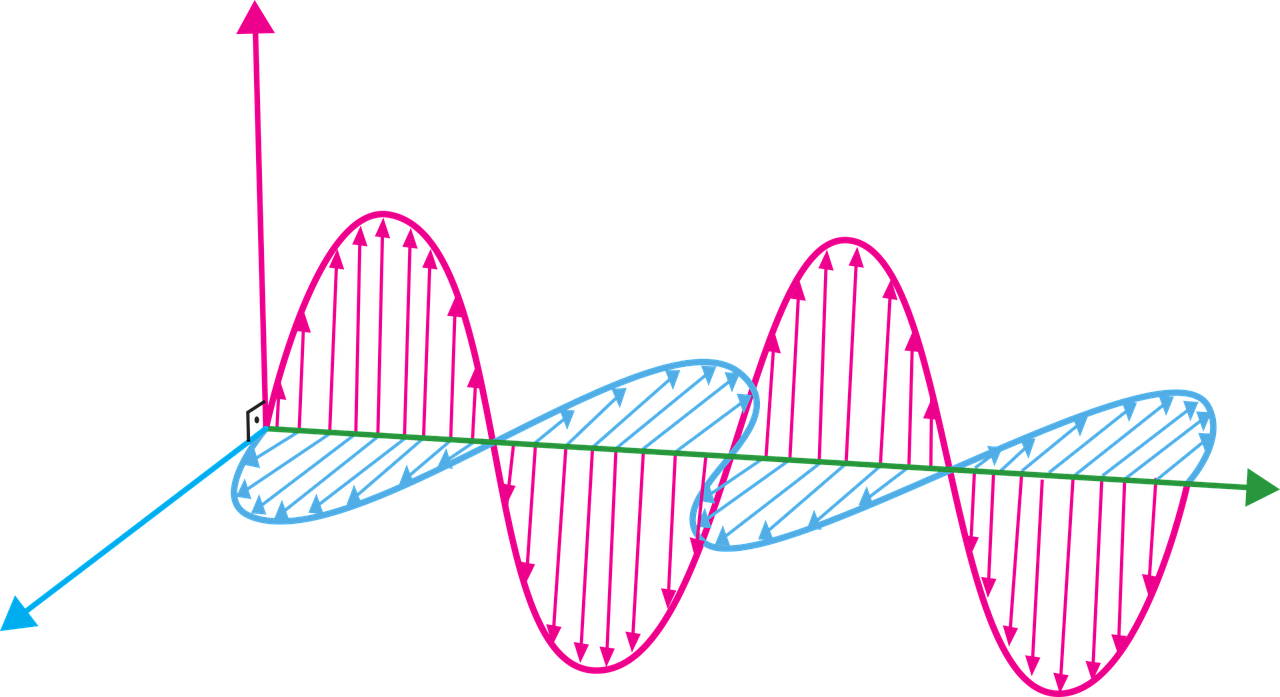

Electromagnetic induction is a fundamental concept in electromagnetism that explains how electric currents can be induced in conductors by changing magnetic fields.
A. Explanation of electromagnetic induction

Electromagnetic induction occurs when a conductor experiences a change in magnetic flux, leading to the generation of an electromotive force (EMF) and the flow of electric current.
B. Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction
Faraday's law states that the magnitude of the induced EMF in a closed loop is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the loop.
According to Faraday ‘s law of electromagnetic Induction
E= – (Nd¢/dt)
C. Lenz’s law
Lenz's law, a corollary to Faraday's law, asserts that the direction of the induced current in a conductor opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it.
D. Applications of electromagnetic induction – Electromagnet and concept of Electromagnetism
The principles of electromagnetic induction find practical applications in devices such as generators, transformers, and induction cooktops, showcasing the versatility and utility of this phenomenon.
What is electromagnetic fields
An electromagnetic field is a physical entity that exerts force on electric charges and magnetic materials within its influence.
Properties of electromagnetic fields
Electromagnetic fields possess characteristics such as strength, direction, and polarity, which determine their interactions with charged particles and magnets.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Electric Field | Produced by electric charges, exerts forces on charged objects. |
| Magnetic Field | Generated by moving charges, interacts with magnets and conductors. |
| Electromagnetic Waves | Formed by oscillating electric and magnetic fields, propagate through space. |
| Maxwell’s Equations | Set of fundamental equations describing electromagnetism. |
Magnetic field lines
Magnetic field lines represent the direction and strength of magnetic fields, forming closed loops around magnets and current-carrying conductors.
Calculating magnetic field strength
The strength of a magnetic field can be quantified using mathematical formulas such as Ampere’s law and the Biot-Savart law, providing insights into the intensity of magnetic forces.
Applications of Electromagnetism

The practical applications of electromagnetism span across various industries, contributing to technological advancements and innovations.
Electromagnets in electric motors
Electromagnets play a vital role in electric motors by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, enabling the operation of machinery and vehicles.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
In the field of medicine, electromagnetism powers MRI machines, allowing for detailed imaging of internal body structures and facilitating diagnostic procedures.
Electromagnetic waves and communication
The transmission of electromagnetic waves, such as radio waves, microwaves, and infrared waves, forms the basis of modern communication systems, including wireless networks and satellite communications.
Electromagnetic levitation
Electromagnetic levitation systems utilize magnetic fields to suspend objects in mid-air, offering potential applications in transportation, maglev trains, and material handling.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a range of electromagnetic waves, each with distinct properties and uses across different fields.
Definition and components of the electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum comprises electromagnetic waves categorized based on their frequencies and wavelengths, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
2. Construction of Electromagnet

2. Construction: Electromagnets are typically made by winding a coil of wire around a magnetic core, such as iron or steel. When current flows through the coil, it creates a magnetic field around the core, turning it into a magnet.
3. Working principle of Electromagnet
3. Working Principle: The working of an electromagnet is based on Ampere’s law, which states that a current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. This magnetic field is strengthened by increasing the number of turns in the coil or by increasing the current flow.
4. Applications of Electromagnet
Electromagnet | Applications of Electromagnet | Description |
1 | Electric Motors | Convert electrical energy into mechanical energy for various industrial uses. |
2 | Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | Medical imaging technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves. |
3 | Magnetic Levitation Trains | Transportation system that uses electromagnets for frictionless movement. |
4 | Loudspeakers | Convert electrical signals into sound waves using electromagnetism. |
5 | Electric Generators | Convert mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. |
6 | Magnetic Locks | Security devices that use electromagnets to control access to doors or gates. |
7 | Maglev Trains | High-speed trains that float above tracks using magnetic levitation. |
8 | Scrapyard Magnets | Lift and move large metallic objects in scrapyards or recycling facilities. |
9 | MRI Machines | Medical equipment that uses strong magnetic fields for detailed imaging. |
10 | Solenoids | Used in various devices such as valves, switches, and relays for control purposes. |
Applications of Electromagnet
4. Applications:
Electromagnets find extensive use in various fields, including:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines in medical diagnostics.
- Magnetic separators for separating ferrous materials in industries.
- Electric motors and generators, where electromagnets are used to create rotating magnetic fields.
- Speakers and headphones, where electromagnets convert electrical signals into sound waves.
- Magnetic levitation (maglev) trains, which use electromagnets to levitate and propel the train.
1. Strength Control
1. Strength Control: One of the significant advantages of electromagnets is their controllable strength. By adjusting the current flow through the coil, the strength of the magnetic field can be precisely controlled, making electromagnets highly adaptable to different requirements.
2. Safety Considerations
2. Safety Considerations: While electromagnets offer many benefits, it’s crucial to handle them with care, especially when dealing with high currents. Proper insulation and cooling mechanisms are essential to prevent overheating and ensure safe operation.
3. Future Development in Electromagnetism
3. Future Developments: Research in electromagnetism continues to advance, leading to innovations such as superconducting electromagnets with near-zero resistance, enhancing efficiency and performance in various applications.
In conclusion, electromagnets play a vital role in modern technology and industry, showcasing the fascinating interplay between electricity and magnetism.
Importance of electromagnetism in modern technology
In today's world, electromagnetism plays a crucial role in numerous technological advancements. From electric motors and generators to communication systems and medical imaging devices, the applications of electromagnetism are vast and diverse.
What are the advantages of using electromagnets in lifting heavy objects?
Electromagnets offer advantages such as adjustable lifting capacity, controlled release of objects, and the ability to operate without direct contact with the load.
Can electromagnets be used underwater or in harsh environments?
Yes, specialized waterproof and ruggedized electromagnets can be used underwater or in harsh environments like industrial settings or marine applications.
What are the advantages of using electromagnets in lifting heavy objects?
Electromagnets offer advantages such as adjustable lifting capacity, controlled release of objects, and the ability to operate without direct contact with the load.
What is an electromagnet?
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current.
How does an electromagnet differ from a permanent magnet?
An electromagnet can be turned on and off by controlling the electric current, while a permanent magnet retains its magnetism without external influence.
What are the components of an electromagnet?
The key components are a coil of wire (usually copper), a core material (often iron or steel), and an electric power source.
What is the principle behind electromagnetism?
Electromagnetism is based on the relationship between electricity and magnetism, where an electric current generates a magnetic field.
How can the strength of an electromagnet be increased?
The strength of an electromagnet can be increased by increasing the number of turns in the coil, using a stronger core material, or increasing the electric current.
What are the applications of electromagnets in daily life?
Electromagnets are used in various applications such as electric motors, speakers, doorbells, MRI machines, and magnetic locks.
What is the role of electromagnets in electric motors?
Electromagnets are used in electric motors to create a rotating magnetic field, which interacts with conductors to produce mechanical motion.
How do electromagnets work in speakers and headphones?
In speakers and headphones, electromagnets interact with a diaphragm or coil to convert electrical signals into sound waves.
What is the importance of electromagnets in MRI machines?
Electromagnets in MRI machines produce strong magnetic fields to create detailed images of internal body structures for medical diagnosis.
How are electromagnets used in magnetic levitation trains?
Electromagnets are used in magnetic levitation trains to create magnetic fields that repel the train from the track, allowing for frictionless movement.
What are the factors affecting the magnetic field of an electromagnet?
Factors include the number of turns in the coil, the strength of the electric current, the core material used, and the coil’s shape and size.
Can an electromagnet lose its magnetism?
Yes, an electromagnet can lose its magnetism when the electric current is turned off or if external factors weaken the magnetic field.
What is the difference between a solenoid and an electromagnet?
A solenoid is a coil of wire used to create a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it, while an electromagnet includes a core material to enhance its magnetic properties.
How are electromagnets used in industrial applications?
Electromagnets are used in industrial applications for lifting heavy loads, sorting metals in recycling facilities, and controlling valves in machinery.
What safety precautions should be followed when working with electromagnets?
Safety precautions include avoiding exposure to strong magnetic fields, using insulated wires, and following proper installation and maintenance procedures.
What is the relationship between electricity and magnetism in electromagnets?
The relationship is described by electromagnetic induction, where electric current produces a magnetic field and changing magnetic fields induce electric currents.
How do scientists measure the strength of an electromagnet?
Scientists measure the strength of electromagnets using devices like gaussmeters or by observing the electromagnet’s lifting capacity for ferromagnetic materials.
What are the advantages of using electromagnets in lifting heavy objects?
Electromagnets offer advantages such as adjustable lifting capacity, controlled release of objects, and the ability to operate without direct contact with the load.
Can electromagnets be used underwater or in harsh environments?
Yes, specialized waterproof and ruggedized electromagnets can be used underwater or in harsh environments like industrial settings or marine applications.
How do electromagnets contribute to the field of robotics?
Electromagnets are used in robotics for gripping and manipulating objects, controlling robotic arms, and enabling precise movements in automated systems.








Dry Cleaning in New York city by Sparkly Maid NYC
Skilled professionals working, expert-level attention to detail. Competent team selected. Skilled satisfaction.
Hello there, I discovered your blog by the use of Google while looking for a related subject, your web site got here up, it seems good. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thanks , I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your site?
This design is spectacular! You certainly know how to keep a reader amused. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Excellent job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
Some genuinely good blog posts on this web site, appreciate it for contribution.
I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thank you again
I genuinely enjoy looking through on this web site, it has superb articles. “Beware lest in your anxiety to avoid war you obtain a master.” by Demosthenes.
As I website owner I conceive the content material here is really fantastic, thankyou for your efforts.
I was wondering if you ever considered changing the structure of your website? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say. But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having 1 or 2 images. Maybe you could space it out better?
I’m not sure exactly why but this website is loading incredibly slow for me. Is anyone else having this problem or is it a issue on my end? I’ll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
Oh my goodness! an amazing article dude. Thanks Nonetheless I’m experiencing situation with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anybody getting similar rss problem? Anybody who knows kindly respond. Thnkx