What is Green house effect – Introduction to the Greenhouse Effect
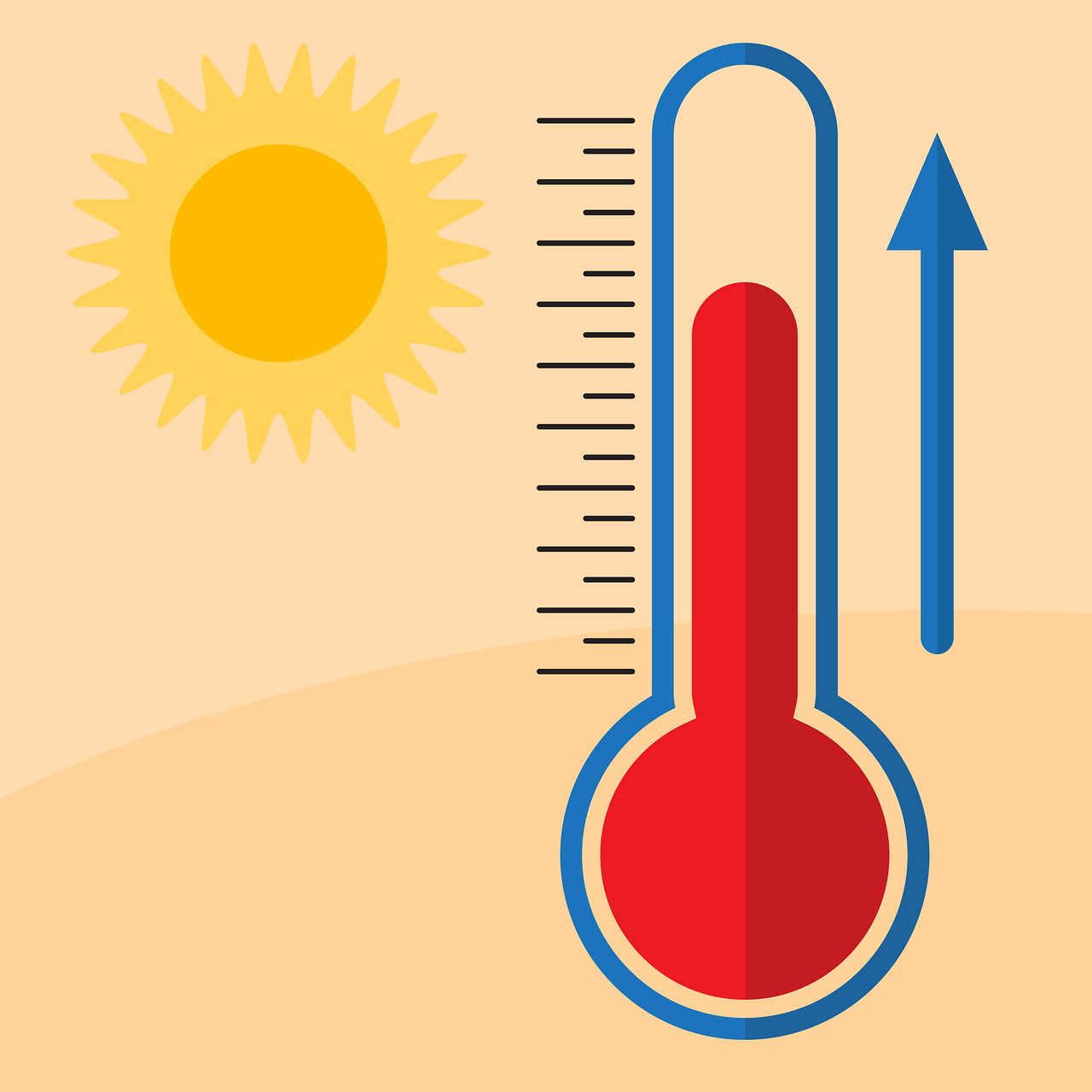
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that plays a crucial role in regulating Earth's temperature. It works by trapping heat in the atmosphere, which helps maintain a suitable climate for life on our planet. Understanding the greenhouse effect is essential as it influences climate patterns, weather conditions, and environmental stability.
- Mastering Chemical Kinetics: In-Depth Guide to Reaction Rates, Mechanisms, and Industrial Applications
- TOP 100 MCQS On Electrical Transformer
- National Creators Award By GOV Of India 2024
Greenhouse Gases and Their Importance
Greenhouse gases are substances that trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to the greenhouse effect. The most common greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor. These gases absorb and re-emit infrared radiation, preventing it from escaping into space and thus warming the planet.
Climate Change and Global Warming

The greenhouse effect is closely linked to climate change and global warming. The excess greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trap more heat, causing temperatures to rise worldwide. This phenomenon results in melting ice caps, rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and shifts in ecosystems, impacting both humans and wildlife.

| Green house effect Question | Green house effect Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the greenhouse effect? | The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. |
| How does the greenhouse effect contribute to global warming? | The greenhouse effect intensifies global warming by trapping heat in the Earth’s atmosphere. |
| What are greenhouse gases, and how do they trap heat in the atmosphere? | Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane trap heat by absorbing and re-emitting infrared radiation. |
| What are the main greenhouse gases responsible for the greenhouse effect? | The main greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor. |
| What role do human activities play in enhancing the greenhouse effect? | Human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation increase greenhouse gas emissions. |
| How does deforestation impact the greenhouse effect? | Deforestation reduces the number of trees that absorb CO2, leading to higher concentrations of greenhouse gases. |
| What are the effects of an intensified greenhouse effect on climate patterns? | An intensified greenhouse effect can cause more extreme weather events, altered precipitation patterns, and shifts in climate zones. |
| How does the greenhouse effect relate to climate change? | The greenhouse effect contributes to climate change by causing a rise in global temperatures and altering weather patterns. |
| What are some natural sources of greenhouse gases? | Natural sources of greenhouse gases include volcanic eruptions, decomposition, and natural vegetation. |
| How do oceans contribute to the greenhouse effect? | Oceans absorb and release CO2, acting as a carbon sink, but they can also release CO2 due to warming, contributing to the greenhouse effect. |
| What are the consequences of an enhanced greenhouse effect on ecosystems? | An enhanced greenhouse effect can lead to habitat loss, species extinction, disrupted ecosystems, and altered migration patterns. |
| How do scientists measure the intensity of the greenhouse effect? | Scientists measure the intensity of the greenhouse effect by analyzing greenhouse gas concentrations, temperature trends, and climate models. |
| What strategies are being implemented to mitigate the greenhouse effect? | Strategies include reducing fossil fuel use, increasing renewable energy adoption, afforestation, and promoting energy-efficient technologies. |
| How does the greenhouse effect impact sea levels and coastal regions? | The greenhouse effect contributes to global warming, which in turn leads to thermal expansion of seawater and melting ice caps, resulting in rising sea levels and coastal erosion. |
| What are the differences between the natural greenhouse effect and the enhanced greenhouse effect caused by human activities? | The natural greenhouse effect maintains Earth’s temperature, while the enhanced effect due to human activities intensifies warming and climate change. |
| What are some examples of feedback mechanisms in the greenhouse effect? | Positive feedback mechanisms include melting ice releasing more CO2 and methane, amplifying the greenhouse effect. Negative feedbacks include increased plant growth absorbing CO2. |
| How does agriculture contribute to greenhouse gas emissions? | Agriculture contributes to emissions through livestock methane, rice cultivation, fertilizer use, and land use changes. |
| What are the implications of the greenhouse effect on weather extremes? | The greenhouse effect can lead to more frequent and intense heatwaves, storms, droughts, floods, and other weather extremes. |
| How do volcanic eruptions influence the greenhouse effect? | Volcanic eruptions can release large amounts of gases and particles into the atmosphere, temporarily cooling the planet but not significantly impacting the long-term greenhouse effect. |
| What are the long-term consequences of ignoring the greenhouse effect? | Ignoring the greenhouse effect can lead to irreversible climate change, ecosystem disruptions, sea level rise, extreme weather events, and socio-economic challenges. |
Bottom line
In conclusion, the greenhouse effect is a natural process essential for maintaining Earth’s temperature. However, human activities have intensified this effect, leading to climate change and global warming. By understanding the greenhouse effect and implementing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient future for generations to come.