CBSE Physics Syllabus Explanation
I’d be happy to help you understand the Class 12 CBSE Physics syllabus in detail. The syllabus typically covers a variety of topics that can be grouped into these chapters:
- Electrostatics
- Current Electricity
- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
- Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Optics
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Atoms and Nuclei
- Electronic Devices
- Communication Systems
Electricity Basics
fully detailed explanation with each important terms & definitions of chapter current & electricity class 12
Supremetutorials would be happy to help you with an overview of the chapter on “Current Electricity” for Class 12. This chapter deals with the flow of electric charges, commonly known as electric current, through conductors.
Electric Current:

Electric current is the flow of electric charges through a conductor. It is measured in Amperes (A) and is denoted by the symbol ‘I’. Current flows from higher potential to lower potential.

Electric Charge (Q):
Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter. It can be positive or negative and is measured in Coulombs (C).
Conductor:
A conductor is a material that allows the easy flow of electric charges. Metals like copper, aluminum, and silver are good conductors.
Insulator:
An insulator is a material that does not allow the easy flow of electric charges. Examples include rubber, plastic, and wood.
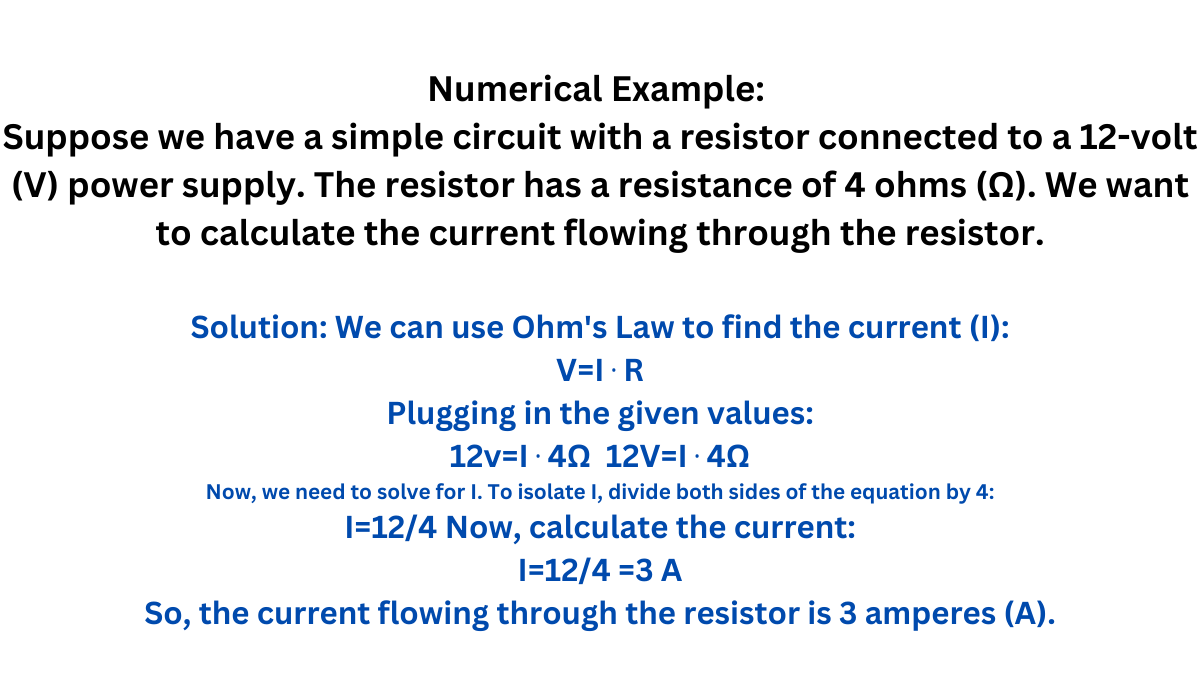
Ohm’s Law:
Ohm’s Law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it and inversely proportional to its resistance.
Mathematically, Ohm’s Law is expressed as:
Where:
I is the current in Amperes (A)
V is the voltage in Volts (V)
R is the resistance in Ohms (Ω)

Resistance (R):
Resistance is the opposition offered by a material to the flow of electric current. It is measured in Ohms (Ω). Different factors like material, length, cross-sectional area, and temperature affect resistance.

Resistivity (ρ):
Resistivity is the inherent property of a material that determines its resistance. It is measured in Ohm-meter (Ω m).
Series and Parallel Combination:
Series Connection: Components are connected end-to-end. The current remains the same, but the voltage divides among the components.
Parallel Connection: Components are connected across the same two points. Voltage remains the same, but the current divides among the components.
Electric Power (P):
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is consumed or produced. It is measured in Watts (W).
P=IV, where
P is power in Watts,
I is current in Amperes, and
V is voltage in Volts.
Kirchhoff’s Laws:
- Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL): The sum of currents entering a junction in a circuit is equal to the sum of currents leaving that junction.
- Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL): The sum of voltages in any closed loop of a circuit is zero.
Ammeter and Voltmeter:
Ammeter: A device used to measure current in a circuit. It is connected in series and has very low resistance.
Voltmeter: A device used to measure voltage across a component. It is connected in parallel and has very high resistance.
Superconductivity:
Superconductivity is a phenomenon where certain materials exhibit zero electrical resistance when cooled below a critical temperature.
CBSE CLASS 12 PHYSICS CHAPTERWISE ANALYSIS
These are some of the key terms and concepts covered in the chapter on Current Electricity for Class 12. Understanding these fundamentals will provide a strong foundation for studying electrical circuits and applications.
Understand The Class 12 CBSE Physics Syllabus In Detail. The Syllabus Typically Covers A Variety Of Topics That Can Be Grouped Into These Chapters:
Electrostatics
Current Electricity
Magnetic Effects Of Current And Magnetism
Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Currents
Electromagnetic Waves
Optics
Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter
Atoms And Nuclei
Electronic Devices
Communication Systems
Each Chapter Explores Specific Concepts Related To The Subject. If You’d Like A More Thorough Explanation Of Any Particular Chapter Or Concept, Please Let Me Know!
- cbse class 12 cbse board physics
Optics:
Optics covers the behavior of light and its interaction with different mediums. Topics include reflection, refraction, lenses, optical instruments, wavefronts, and Huygens’ principle.
Write ” Class 12 Cbse board physics syllabus in detail with chapters full explanation plagiarism free”
I’d be happy to help you understand the Class 12 CBSE Physics syllabus in detail. The syllabus typically covers a variety of topics that can be grouped into these chapters:
Electrostatics
Current Electricity
Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
Electromagnetic Waves
Optics
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Atoms and Nuclei
Electronic Devices
Communication Systems
Each chapter explores specific concepts related to the subject. If you’d like a more thorough explanation of any particular chapter or concept, please let me know!
Electrostatics:
This chapter deals with the study of electric charges, their properties, and behavior. It covers topics like Coulomb’s law, electric field and potential, Gauss’s law, electric dipole, and capacitors.
Current Electricity:
This chapter focuses on the flow of electric current in conductors. It covers Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s laws, electrical resistance, and various types of circuits including series and parallel.
Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism:
Here, you’ll study the connection between electric current and magnetic fields. This includes topics like the magnetic field due to a current-carrying conductor, Ampere’s law, and magnetic properties of materials.
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents:
This chapter introduces electromagnetic induction and the generation of induced EMF. It also covers topics like Faraday’s law, Lenz’s law, self-inductance, mutual inductance, and AC circuits.
Electromagnetic Waves:
Electromagnetic waves like light are discussed in this chapter. You’ll learn about their characteristics, propagation, and properties, including topics like electromagnetic spectrum and their applications.
Optics:
Optics covers the behavior of light and its interaction with different mediums. Topics include reflection, refraction, lenses, optical instruments, wavefronts, and Huygens’ principle.
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter:
This chapter delves into the dual nature of particles, particularly electrons, as both particles and waves. It covers topics like photoelectric effect, de Broglie wavelength, and matter waves.
Atoms and Nuclei:
The structure of atoms and their nuclei are explored here. Topics include atomic models, Bohr’s theory, energy levels, radioactivity, nuclear reactions, and the fundamental forces within nuclei.
Electronic Devices:
This chapter focuses on semiconductor devices and their applications. You’ll study diodes, transistors, logic gates, and digital electronics.
Communication Systems:
This chapter deals with various aspects of communication, including modulation and demodulation of signals. It covers topics like amplitude modulation, frequency modulation, and basic components of a communication system.
Remember, each chapter in the CBSE syllabus builds upon the previous ones and provides a comprehensive understanding of physics concepts. If you have specific questions about any of these chapters or need more detailed explanations, feel free to ask!
I’d be happy to help you understand the Class 12 CBSE Physics syllabus in detail. The syllabus typically covers a variety of topics that can be grouped into these chapters:
Electrostatics
Current Electricity
Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
Electromagnetic Waves
Optics
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Atoms and Nuclei
Electronic Devices
Communication Systems
Each chapter explores specific concepts related to the subject. If you’d like a more thorough explanation of any particular chapter or concept, please let me know!
Absolutely, I’d be glad to provide a brief overview of each chapter in the Class 12 CBSE Physics syllabus:
Electrostatics:
This chapter deals with the study of electric charges, their properties, and behavior. It covers topics like Coulomb’s law, electric field and potential, Gauss’s law, electric dipole, and capacitors.
Current Electricity:
This chapter focuses on the flow of electric current in conductors. It covers Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s laws, electrical resistance, and various types of circuits including series and parallel.
Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism:
Here, you’ll study the connection between electric current and magnetic fields. This includes topics like the magnetic field due to a current-carrying conductor, Ampere’s law, and magnetic properties of materials.
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents:
This chapter introduces electromagnetic induction and the generation of induced EMF. It also covers topics like Faraday’s law, Lenz’s law, self-inductance, mutual inductance, and AC circuits.
Electromagnetic Waves:
Electromagnetic waves like light are discussed in this chapter. You’ll learn about their characteristics, propagation, and properties, including topics like electromagnetic spectrum and their applications.
Optics:
Optics covers the behavior of light and its interaction with different mediums. Topics include reflection, refraction, lenses, optical instruments, wavefronts, and Huygens’ principle.
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter:
This chapter delves into the dual nature of particles, particularly electrons, as both particles and waves. It covers topics like photoelectric effect, de Broglie wavelength, and matter waves.
Atoms and Nuclei:
The structure of atoms and their nuclei are explored here. Topics include atomic models, Bohr’s theory, energy levels, radioactivity, nuclear reactions, and the fundamental forces within nuclei.
Electronic Devices:
This chapter focuses on semiconductor devices and their applications. You’ll study diodes, transistors, logic gates, and digital electronics.
Communication Systems:
This chapter deals with various aspects of communication, including modulation and demodulation of signals. It covers topics like amplitude modulation, frequency modulation, and basic components of a communication system.
Current Electricity:
This chapter focuses on the flow of electric current in conductors. It covers Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s laws, electrical resistance, and various types of circuits including series and parallel.
Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism:
Here, you’ll study the connection between electric current and magnetic fields. This includes topics like the magnetic field due to a current-carrying conductor, Ampere’s law, and magnetic properties of materials.
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents:
This chapter introduces electromagnetic induction and the generation of induced EMF. It also covers topics like Faraday’s law, Lenz’s law, self-inductance, mutual inductance, and AC circuits.
Electromagnetic Waves:
Electromagnetic waves like light are discussed in this chapter. You’ll learn about their characteristics, propagation, and properties, including topics like electromagnetic spectrum and their applications.
Optics:
Optics covers the behavior of light and its interaction with different mediums. Topics include reflection, refraction, lenses, optical instruments, wavefronts, and Huygens’ principle.
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter:
This chapter delves into the dual nature of particles, particularly electrons, as both particles and waves. It covers topics like photoelectric effect, de Broglie wavelength, and matter waves.
Atoms and Nuclei:
The structure of atoms and their nuclei are explored here. Topics include atomic models, Bohr’s theory, energy levels, radioactivity, nuclear reactions, and the fundamental forces within nuclei.
Electronic Devices:
This chapter focuses on semiconductor devices and their applications. You’ll study diodes, transistors, logic gates, and digital electronics.
Communication Systems:
This chapter deals with various aspects of communication, including modulation and demodulation of signals. It covers topics like amplitude modulation, frequency modulation, and basic components of a communication system.
Remember, each chapter in the CBSE syllabus builds upon the previous ones and provides a comprehensive understanding of physics concepts. If you have specific questions about any of these chapters or need more detailed explanations, feel free to ask!
Certainly, let’s delve deeper into each chapter of the Class 12 CBSE Physics syllabus:
Electrostatics:
Coulomb’s Law: Describes the force between two point charges. The force is directly proportional to the product of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Electric Field: The region around a charge where other charges experience a force. Electric field lines depict its direction and strength.
Gauss’s Law: Relates the electric flux through a closed surface to the charge enclosed. Useful for calculating electric fields in symmetric systems.
Electric Potential: The work done to bring a unit positive charge from infinity to a point in an electric field. Potential difference determines how energy moves charges.
Capacitors: Devices that store electric charge and energy. The capacitance depends on the geometry of conductors and dielectric material.
Current Electricity:
Ohm’s Law: Describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance (V = IR).
Kirchhoff’s Laws: Rules for analyzing complex circuits. Kirchhoff’s current law deals with junctions, while Kirchhoff’s voltage law deals with loops.
Electrical Resistance: Resistance in a conductor depends on its dimensions, resistivity, and temperature.
Series and Parallel Circuits: Different arrangements of resistors that affect current and voltage distribution.
Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism:
Magnetic Field due to Current: A current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. Right-hand thumb rule helps determine field direction.
Ampere’s Law: Relates magnetic field and current in a closed loop.
Magnetic Properties of Materials: Diamagnetic, paramagnetic, and ferromagnetic substances respond differently to magnetic fields.
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents:
Faraday’s Law: Changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) and hence current in a circuit.
Lenz’s Law: The induced EMF opposes the change causing it.
Self-Inductance: A changing current in a coil induces an EMF in the same coil.
Mutual Inductance: Changing current in one coil induces EMF in another nearby coil.
AC Circuits: Alternating current and voltage, RMS value, reactance, impedance, and power factor.
Electromagnetic Waves:
Electromagnetic Spectrum: Range of electromagnetic waves from radio waves to gamma rays.
Characteristics of Electromagnetic Waves: They travel through a vacuum, have a constant speed (speed of light), and exhibit transverse waves.
Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves: Reflect, refract, diffract, and polarize.
Optics:
Reflection: Laws of reflection and image formation in plane mirrors.
Refraction: Snell’s law, refractive index, and image formation in lenses.
Lenses: Convex and concave lenses, lens formula, and magnification.
Optical Instruments: Microscopes, telescopes, and their working principles.
Huygens’ Principle: Each point of a wavefront acts as a source of secondary waves.
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter:
Photoelectric Effect: Emission of electrons from a metal surface when light of sufficient frequency strikes it. Explained using photons and energy conservation.
de Broglie Wavelength: Particles, especially electrons, exhibit wave-like behavior. Wavelength depends on momentum.
Davisson-Germer Experiment: Confirmed the wave-like nature of electrons using diffraction.
Atoms and Nuclei:
Atomic Models: Bohr’s model explains the hydrogen atom’s spectral lines.
Energy Levels: Electrons occupy discrete energy levels around the nucleus.
Radioactivity: Spontaneous decay of unstable nuclei, involving alpha, beta, and gamma radiation.
Nuclear Reactions: Fusion and fission processes.
Fundamental Forces: Strong, weak, electromagnetic, and gravitational forces within nuclei.
Electronic Devices:
Semiconductors: Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors.
Diodes: P-N junction behavior, forward and reverse biasing.
Transistors: NPN and PNP transistors, transistor as an amplifier and a switch.
Logic Gates: Basic building blocks of digital circuits.
Communication Systems:
Modulation: Process of superimposing the message signal on a carrier signal.
Demodulation: Recovering the original signal from the modulated carrier.
Amplitude Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM): Different modulation techniques used in radio communication.
CBSE Physics Syllabus Explanation
Electrostatics
Current Electricity
Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
Electromagnetic Waves
Optics
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Atoms and Nuclei
Electronic Devices
Communication Systems
Each chapter explores specific concepts related to the subject. If you’d like a more thorough explanation of any particular chapter or concept, please let me know!
a brief overview of each chapter in the Class 12 CBSE Physics syllabus:
Electrostatics:
This chapter deals with the study of electric charges, their properties, and behavior. It covers topics like Coulomb’s law, electric field and potential, Gauss’s law, electric dipole, and capacitors.
Current Electricity:
This chapter focuses on the flow of electric current in conductors. It covers Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s laws, electrical resistance, and various types of circuits including series and parallel.
Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism:
Here, you’ll study the connection between electric current and magnetic fields. This includes topics like the magnetic field due to a current-carrying conductor, Ampere’s law, and magnetic properties of materials.
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents:
This chapter introduces electromagnetic induction and the generation of induced EMF. It also covers topics like Faraday’s law, Lenz’s law, self-inductance, mutual inductance, and AC circuits.
Electromagnetic Waves:
Electromagnetic waves like light are discussed in this chapter. You’ll learn about their characteristics, propagation, and properties, including topics like electromagnetic spectrum and their applications.
Optics:
Optics covers the behavior of light and its interaction with different mediums. Topics include reflection, refraction, lenses, optical instruments, wavefronts, and Huygens’ principle.
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter:
This chapter delves into the dual nature of particles, particularly electrons, as both particles and waves. It covers topics like photoelectric effect, de Broglie wavelength, and matter waves.
Atoms and Nuclei:
The structure of atoms and their nuclei are explored here. Topics include atomic models, Bohr’s theory, energy levels, radioactivity, nuclear reactions, and the fundamental forces within nuclei.
Electronic Devices:
This chapter focuses on semiconductor devices and their applications. You’ll study diodes, transistors, logic gates, and digital electronics.
Communication Systems:
This chapter deals with various aspects of communication, including modulation and demodulation of signals. It covers topics like amplitude modulation, frequency modulation, and basic components of a communication system.
Remember, each chapter in the CBSE syllabus builds upon the previous ones and provides a comprehensive understanding of physics concepts. If you have specific questions about any of these chapters or need more detailed explanations, feel free to ask!
Electrostatics:
Coulomb’s Law: Describes the force between two point charges. The force is directly proportional to the product of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Electric Field: The region around a charge where other charges experience a force. Electric field lines depict its direction and strength.
Gauss’s Law: Relates the electric flux through a closed surface to the charge enclosed. Useful for calculating electric fields in symmetric systems.
Electric Potential: The work done to bring a unit positive charge from infinity to a point in an electric field. Potential difference determines how energy moves charges.
Capacitors: Devices that store electric charge and energy. The capacitance depends on the geometry of conductors and dielectric material.
Current Electricity:
Ohm’s Law: Describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance (V = IR).
Kirchhoff’s Laws: Rules for analyzing complex circuits. Kirchhoff’s current law deals with junctions, while Kirchhoff’s voltage law deals with loops.
Electrical Resistance: Resistance in a conductor depends on its dimensions, resistivity, and temperature.
Series and Parallel Circuits: Different arrangements of resistors that affect current and voltage distribution.
Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism:
Magnetic Field due to Current: A current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. Right-hand thumb rule helps determine field direction.
Ampere’s Law: Relates magnetic field and current in a closed loop.
Magnetic Properties of Materials: Diamagnetic, paramagnetic, and ferromagnetic substances respond differently to magnetic fields.
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents:
Faraday’s Law: Changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) and hence current in a circuit.
Lenz’s Law: The induced EMF opposes the change causing it.
Self-Inductance: A changing current in a coil induces an EMF in the same coil.
Mutual Inductance: Changing current in one coil induces EMF in another nearby coil.
AC Circuits: Alternating current and voltage, RMS value, reactance, impedance, and power factor.
Electromagnetic Waves:
Electromagnetic Spectrum: Range of electromagnetic waves from radio waves to gamma rays.
Characteristics of Electromagnetic Waves: They travel through a vacuum, have a constant speed (speed of light), and exhibit transverse waves.
Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves: Reflect, refract, diffract, and polarize.
Optics:
Reflection: Laws of reflection and image formation in plane mirrors.
Refraction: Snell’s law, refractive index, and image formation in lenses.
Lenses: Convex and concave lenses, lens formula, and magnification.
Optical Instruments: Microscopes, telescopes, and their working principles.
Huygens’ Principle: Each point of a wavefront acts as a source of secondary waves.
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter:
Photoelectric Effect: Emission of electrons from a metal surface when light of sufficient frequency strikes it. Explained using photons and energy conservation.
de Broglie Wavelength: Particles, especially electrons, exhibit wave-like behavior. Wavelength depends on momentum.
Davisson-Germer Experiment: Confirmed the wave-like nature of electrons using diffraction.
Atoms and Nuclei:
Atomic Models: Bohr’s model explains the hydrogen atom’s spectral lines.
Energy Levels: Electrons occupy discrete energy levels around the nucleus.
Radioactivity: Spontaneous decay of unstable nuclei, involving alpha, beta, and gamma radiation.
Nuclear Reactions: Fusion and fission processes.
Fundamental Forces: Strong, weak, electromagnetic, and gravitational forces within nuclei.
Electronic Devices:
Semiconductors: Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors.
Diodes: P-N junction behavior, forward and reverse biasing.
Transistors: NPN and PNP transistors, transistor as an amplifier and a switch.
Logic Gates: Basic building blocks of digital circuits.
Communication Systems:
Modulation: Process of superimposing the message signal on a carrier signal.
Demodulation: Recovering the original signal from the modulated carrier.
Amplitude Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM): Different modulation techniques used in radio communication.
Remember that these explanations provide a broad understanding of each chapter’s topics. If you need more specific details or further clarification on any concept, feel free to ask!
Certainly, let’s delve into a more detailed explanation of the first chapter: Electrostatics.
1. Electrostatics:
Coulomb’s Law:
Coulomb’s law states that the force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their magnitudes and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Mathematically, it can be represented as:
F = k * (|q1 * q2|) / r^2
Where:
F is the force between the charges q1 and q2.
k is Coulomb’s constant.
r is the distance between the charges.
Electric Field:
The electric field at a point is the force experienced by a positive test charge placed at that point. It’s defined as the force per unit positive charge. Mathematically, it’s given by:
E = F / q
Where:
E is the electric field.
F is the force experienced by the test charge.
q is the magnitude of the test charge.
Gauss’s Law:
Gauss’s law relates the electric flux through a closed surface to the charge enclosed within the surface. Mathematically, it’s expressed as:
Φ = q / ε₀
Where:
Φ is the electric flux.
q is the total charge enclosed.
ε₀ is the vacuum permittivity.
Electric Potential:
The electric potential at a point is the work done in bringing a unit positive charge from infinity to that point. It’s measured in volts (V). The potential difference (voltage) between two points is given by:
V = W / q
Where:
V is the potential difference.
W is the work done.
q is the magnitude of the charge.
Capacitors:
Capacitors store electric charge and energy. The capacitance (C) of a capacitor is defined as the ratio of the charge stored (q) to the potential difference (V) across its plates:
C = q / V
Capacitance depends on the geometry of the conductors and the material between them. It’s measured in farads (F).
Example:
Let’s consider two point charges, q1 = 4 μC and q2 = -3 μC, placed 2 meters apart. Using Coulomb’s law, we can calculate the force between them:
F = k * (|q1 * q2|) / r^2
F = (9 × 10^9 N m²/C²) * (|4 × 10^-6 C * -3 × 10^-6 C|) / (2 m)^2
F = 13.5 N
This force would be attractive since the charges have opposite signs.





There most be a solution for this problem, some people think there will be now solutions, but i think there wil be one.
Your style is very unique in comparison to other folks I have read stuff from. Thank you for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I will just bookmark this page.
I must thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this website. I’m hoping to view the same high-grade content from you later on as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my very own site now 😉
The next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesn’t disappoint me just as much as this particular one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, however I really believed you would have something useful to say. All I hear is a bunch of complaining about something that you can fix if you weren’t too busy searching for attention.
Hey there! I just want to offer you a huge thumbs up for your great info you have got right here on this post. I’ll be coming back to your blog for more soon.
There is certainly a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you have made.
This page definitely has all of the information I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
This is a great tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere. Brief but very precise info… Many thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.
This website truly has all the information and facts I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Loving the info on this website , you have done outstanding job on the blog posts.
Can I just say what a relief to find someone that genuinely understands what they are talking about on the web. You certainly understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people really need to read this and understand this side of your story. I can’t believe you’re not more popular given that you definitely have the gift.
When I initially left a comment I appear to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I receive four emails with the exact same comment. Perhaps there is a means you are able to remove me from that service? Thanks.
Hi there! This blog post could not be written any better! Reading through this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He constantly kept talking about this. I am going to send this information to him. Pretty sure he will have a great read. Thank you for sharing!
You are so interesting! I do not suppose I have read something like that before. So wonderful to find another person with some genuine thoughts on this subject matter. Seriously.. many thanks for starting this up. This site is something that is needed on the web, someone with a bit of originality.
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular article! It is the little changes that will make the most significant changes. Thanks for sharing!
Thanks for the sensible critique. Me and my neighbor were just preparing to do a little research on this. We got a grab a book from our area library but I think I learned more clear from this post. I’m very glad to see such wonderful info being shared freely out there.
This is a topic that is near to my heart… Take care! Exactly where are your contact details though?
I blog often and I truly appreciate your content. The article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to book mark your site and keep checking for new information about once a week. I subscribed to your RSS feed too.
I need to to thank you for this good read!! I certainly loved every bit of it. I have got you saved as a favorite to check out new things you post…
I would like to thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this blog. I am hoping to see the same high-grade content by you later on as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my very own website now 😉
I blog quite often and I seriously thank you for your content. The article has truly peaked my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information about once a week. I opted in for your RSS feed as well.
Your style is really unique in comparison to other folks I’ve read stuff from. Thank you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I will just bookmark this blog.
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a co-worker who was doing a little research on this. And he actually ordered me lunch simply because I found it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending some time to talk about this topic here on your web page.
I used to be able to find good information from your blog articles.
This is a topic that’s near to my heart… Thank you! Where are your contact details though?
I was able to find good advice from your blog articles.
Genuinely appreciated perusing this entry. It’s extremely clear and filled with valuable details. Thank you for sharing this.
Good day! I just wish to offer you a huge thumbs up for the excellent information you’ve got here on this post. I am returning to your site for more soon.
Having read this I thought it was really enlightening. I appreciate you finding the time and energy to put this article together. I once again find myself personally spending a lot of time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worthwhile.
Your style is so unique compared to other people I’ve read stuff from. Thank you for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I will just bookmark this blog.
This is a topic which is close to my heart… Many thanks! Exactly where are your contact details though?
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I really like it when individuals get together and share thoughts. Great website, stick with it.
Local building codes here in Pierce County require you to manage runoff responsibly, so a properly sloped gutter system keeps foundations safe and neighbors happy. We recycle all old metal so Tacoma’s landfills stay lighter and your project leaves a greener footprint on the Pacific Northwest we all love. With rain coming sideways across Commencement Bay, hidden drip‑edge flashing stops water from sneaking behind the fascia and into your attic insulation.
An interesting discussion is definitely worth comment. I do believe that you should publish more on this subject, it may not be a taboo subject but generally folks don’t discuss such issues. To the next! Cheers.
Your style is unique in comparison to other people I’ve read stuff from. Many thanks for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I will just bookmark this page.
Appreciated the details in this article. It’s highly well-researched and filled with helpful information. Great effort!
I really like it when individuals come together and share ideas. Great website, stick with it!
My coder is trying to convince me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using WordPress on numerous websites for about a year and am nervous about switching to another platform. I have heard great things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can import all my wordpress posts into it? Any help would be really appreciated!
This is a great tip especially to those fresh to the blogosphere. Brief but very precise information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read post!
After I originally commented I seem to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now whenever a comment is added I recieve four emails with the exact same comment. Perhaps there is a means you can remove me from that service? Thanks a lot.
After checking out a number of the blog articles on your website, I seriously appreciate your way of writing a blog. I book marked it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back soon. Please check out my website too and let me know what you think.
Right here is the perfect blog for anybody who would like to find out about this topic. You know so much its almost tough to argue with you (not that I personally will need to…HaHa). You certainly put a fresh spin on a topic that’s been written about for many years. Excellent stuff, just excellent.
I would like to thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this site. I am hoping to view the same high-grade content by you in the future as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own website now 😉
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a friend who was doing a little homework on this. And he actually bought me dinner simply because I discovered it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending the time to talk about this topic here on your blog.
Very good information. Lucky me I ran across your site by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve saved as a favorite for later!
I couldn’t refrain from commenting. Very well written!
You ought to take part in a contest for one of the most useful websites online. I am going to highly recommend this blog!
Pretty! This was an incredibly wonderful post. Thanks for supplying this information.
Hello! I just would like to offer you a big thumbs up for the great info you have right here on this post. I am coming back to your web site for more soon.
You should be a part of a contest for one of the greatest websites on the net. I most certainly will highly recommend this site!
This website definitely has all of the info I wanted about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Good info. Lucky me I discovered your website by accident (stumbleupon). I have bookmarked it for later!
I needed to thank you for this wonderful read!! I definitely enjoyed every bit of it. I’ve got you bookmarked to check out new things you post…
Ótima compra. Muito feliz com o resultado.
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to come back yet again since I saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.
This site really has all the information and facts I wanted about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Right here is the right webpage for anybody who would like to understand this topic. You understand a whole lot its almost tough to argue with you (not that I really will need to…HaHa). You definitely put a fresh spin on a subject that has been written about for ages. Wonderful stuff, just wonderful.
Everything is very open with a clear clarification of the challenges. It was really informative. Your site is very helpful. Thank you for sharing!
Greetings! Very helpful advice in this particular post! It’s the little changes that make the greatest changes. Many thanks for sharing!
Excellent web site you have here.. It’s difficult to find good quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! Take care!!
Wonderful article! We are linking to this great content on our website. Keep up the great writing.
Aw, this was a very nice post. In idea I wish to put in writing like this moreover taking time and precise effort to make an excellent article! I procrastinate alot and by no means seem to get something done.
I think I will become a great follower.Just want to say your post is striking. The clarity in your post is simply striking and i can take for granted you are an expert on this subject.
A motivating discussion is worth comment. I do believe that you need to write more about this topic, it may not be a taboo subject but usually folks don’t talk about such subjects. To the next! Kind regards.
I blog frequently and I truly thank you for your information. The article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to bookmark your blog and keep checking for new details about once per week. I opted in for your Feed as well.
I couldn’t resist commenting. Exceptionally well written.
Can I simply just say what a relief to uncover a person that truly understands what they are talking about on the internet. You definitely understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More and more people ought to check this out and understand this side of the story. I was surprised you are not more popular given that you surely have the gift.
The very next time I read a blog, I hope that it does not fail me just as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, however I truly thought you would probably have something interesting to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could fix if you weren’t too busy seeking attention.
After exploring a number of the articles on your site, I truly like your way of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Take a look at my web site as well and tell me what you think.
thanks
thanks
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon every day. It will always be interesting to read articles from other authors and use a little something from their web sites.
You need to be a part of a contest for one of the most useful sites on the net. I am going to highly recommend this website!
This page really has all the information and facts I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
I like to spend my free time by scanning various internet resources. Today I came across your website and I found it has some of the most practical and helpful information I’ve seen.
thanks
It is perfect time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could I want to suggest you some interesting things or suggestions. Perhaps you can write next articles referring to this article. I wish to read more things about it!
Genuinely enjoyed this entry. It gave tons of useful insights. Excellent effort on creating this.
This excellent website certainly has all of the information and facts I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you writing this write-up and also the rest of the website is extremely good.
thanks
This is a really good tip especially to those fresh to the blogosphere. Short but very accurate info… Thank you for sharing this one. A must read post!
This is a topic that is near to my heart… Take care! Exactly where are your contact details though?
I used to be able to find good info from your blog posts.
Can I simply just say what a comfort to find an individual who truly knows what they’re discussing on the internet. You actually know how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people ought to look at this and understand this side of your story. I was surprised that you’re not more popular because you definitely possess the gift.
Very good info. Lucky me I discovered your site by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve bookmarked it for later.
Unquestionably believe that which you stated. Your favorite reason appeared to be on the net the easiest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I certainly get irked while people consider worries that they plainly don’t know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top and defined out the whole thing without having side-effects , people could take a signal. Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
A thoughtful insight and ideas I will use on my blog. You’ve obviously spent some time on this. Congratulations
I was able to find good information from your articles.
I wanted to check up and let you know how, a great deal I cherished discovering your blog today. I might consider it an honor to work at my office and be able to utilize the tips provided on your blog and also be a part of visitors’ reviews like this. Should a position associated with guest writer become on offer at your end, make sure you let me know.
This is a topic which is near to my heart… Thank you! Exactly where can I find the contact details for questions?
This site was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something that helped me. Thank you.
HBet – Cổng giải trí trực tuyến hàng đầu, quy tụ hàng ngàn trò chơi cá cược thể thao, casino, slot game và bắn cá đổi thưởng. Giao diện mượt mà, bảo mật tuyệt …
Could not disagree with the main ideas. Wonder how things will develop over the coming years.
An interesting discussion is definitely worth comment. I think that you need to write more about this subject, it might not be a taboo matter but usually people do not speak about these issues. To the next! All the best!
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Thanks, However I am encountering difficulties with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I cannot subscribe to it. Is there anybody having similar RSS issues? Anyone that knows the answer can you kindly respond? Thanx!
I would like to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this site. I really hope to check out the same high-grade content by you in the future as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own site now 😉
Local building codes here in Pierce County require you to manage runoff responsibly, so a properly sloped gutter system keeps foundations safe and neighbors happy. With rain coming sideways across Commencement Bay, hidden drip‑edge flashing stops water from sneaking behind the fascia and into your attic insulation. Choosing 6‑inch K‑style aluminum troughs means up to 40 percent more water moves away from your roof, preventing the dreaded waterfall effect in heavy downpours.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve visited this blog before but after browsing through some of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely happy I stumbled upon it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back often!
That is a very good tip especially to those new to the blogosphere. Brief but very precise info… Many thanks for sharing this one. A must read post.
I wanted to thank you for this wonderful read!! I definitely loved every little bit of it. I have got you book marked to look at new stuff you post…
This excellent website definitely has all the information and facts I wanted about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
When I originally commented I appear to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on whenever a comment is added I receive 4 emails with the same comment. Perhaps there is a way you are able to remove me from that service? Thanks.
It is perfect time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could I want to suggest you some interesting things or suggestions. Perhaps you can write next articles referring to this article. I wish to read more things about it!
Have you always been concerned about these issues?
Hello there! This post couldn’t be written much better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He constantly kept preaching about this. I am going to send this information to him. Pretty sure he’ll have a good read. Many thanks for sharing!
Amazing blog! Do you have any suggestions for aspiring writers? I’m hoping to start my own site soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you suggest starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many options out there that I’m completely overwhelmed .. Any ideas? Appreciate it!
Can I just say what a relief to discover a person that really knows what they’re talking about over the internet. You certainly understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. A lot more people have to read this and understand this side of your story. I can’t believe you are not more popular since you surely have the gift.
This is a topic that’s close to my heart… Best wishes! Exactly where are your contact details though?
nail support formula that uses cutting-edge nanotechnology to rejuvenate and restore health from within.
Homeowners across Proctor District rave that our color‑matched downspouts actually enhance curb appeal instead of looking like cheap after‑thoughts. Proper downspout extensions send runoff well past your flowerbeds so you spend weekends gardening instead of dealing with muddy erosion trenches. Local building codes here in Pierce County require you to manage runoff responsibly, so a properly sloped gutter system keeps foundations safe and neighbors happy.
Very good product! Perfect.
Wonderful paintings! This is the kind of info that are meant to be shared across the net. Disgrace on search engines for no longer positioning this publish upper! Come on over and talk over with my website . Thank you =)
vanity leads to more plastic surgery procedures. people are becoming more conscious about their appearance-
Appreciated this post. It’s extremely detailed and packed with useful information. Fantastic job!
Spot on with this write-up, I really think this site needs a lot more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read through more, thanks for the advice.
This is amazing! Filled with useful details and very well-written. Thank you for providing this.
Have you always been concerned about these issues?
Beneficial Blog! I seemed to be simply discussing that there are lots screwy outcomes in the issue you now solely changed my own perception. Thank you really significantly an ideal write-up
Dry Cleaning in New York city by Sparkly Maid NYC
Can I simply say what a relief to seek out somebody who actually knows what theyre speaking about on the internet. You definitely know tips on how to deliver a problem to gentle and make it important. Extra people must learn this and understand this facet of the story. I cant consider youre no more in style since you undoubtedly have the gift.
You seem to be very professional in the way you write,
This web site certainly has all the info I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Totally worth it. Efficient.
I love it when people get together and share thoughts. Great website, keep it up.
The next time I read a blog, Hopefully it does not disappoint me just as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read through, nonetheless I really believed you would probably have something useful to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could possibly fix if you weren’t too busy looking for attention.
Can I just say what a relief to search out somebody who really is aware of what theyre speaking about on the internet. You undoubtedly know how to deliver a problem to light and make it important. Extra folks need to learn this and perceive this facet of the story. I cant consider youre no more common because you positively have the gift.
After exploring a number of the blog posts on your blog, I seriously appreciate your technique of blogging. I book-marked it to my bookmark site list and will be checking back in the near future. Please check out my web site as well and let me know your opinion.
Our team uses hidden screw‑in hangers that lock gutters to the rafter tails, outclassing the rusty spike-and-ferrule setups you still see on too many older homes. Annual tune‑ups are available; we flush, reseal corners and adjust hangers so your system keeps working even after the roughest winter freeze–thaw cycles. Every installation comes with stainless steel micro‑mesh guards that laugh at fir needles, keeping maintenance low even during those blustery November storms.
Welcome to NanoDefense Pro is the official website of a powerful supplement that is an advanced skincare and nail support formula that uses cutting-edge nanotechnology to rejuvenate and restore health from within.
An interesting discussion will probably be worth comment. I’m sure you should write regarding this topic, may well be a taboo subject but generally people are too little to communicate on such topics. To a higher. Cheers
Really liked it! Definitely I’ll buy it again.
This is a topic which is close to my heart… Take care! Where can I find the contact details for questions?
Great post. I was checking constantly this blog and I’m impressed! Very useful info specifically the last part 🙂 I care for such info much. I was looking for this certain information for a very long time. Thank you and good luck.
Saved as a favorite, I love your website!
Hello there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this website before but after looking at many of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m certainly pleased I found it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back frequently!
Saved as a favorite, I like your site!
Primera is a modern supplement designed to support pelvic health. It uses selected natural ingredients to improve bladder control and help urinary tract health while focusing on overall pelvic wellness.
Tak, możliwe wewnętrzne transfery środków między kontami Moracon Ltd., Strovolou 213, 3062, Nikozja (Cypr). Historia Vavada rozpoczęła się w 2017 roku, gdy grupa doświadczonych graczy postanowiła stworzyć „idealne kasyno online”.
Performance-driven cleaning, results-driven approach works. Results-based relationship. Performance excellence.
Looking forward to your next post.
Very helpful article – appreciate your time!
Good points raised here.
This answered a lot of my questions.
Great job simplifying this topic.
You ought to take part in a contest for one of the highest quality blogs on the web. I’m going to recommend this blog!
This is fantastic. I picked up a lot from reading it. The information is very informative and arranged.
Great entry. I thought the information highly useful. Appreciated the method you explained all the points.
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to revisit once again since i have book marked it. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to help others.
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful article. Thanks for supplying this information.
After I originally left a comment I seem to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on each time a comment is added I recieve 4 emails with the same comment. Perhaps there is a way you can remove me from that service? Cheers.
I was very pleased to uncover this website. I need to to thank you for your time for this fantastic read!! I definitely liked every bit of it and i also have you saved to fav to see new information in your web site.
I need to to thank you for this excellent read!! I definitely enjoyed every little bit of it. I’ve got you book-marked to check out new things you post…
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to come back yet again since I book marked it. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide others.
dafabetvn.pro đội ngũ hỗ trợ chuyên nghiệp 24/7
sun52.life là địa chỉ giải trí đáng tin cậy
ee88.io đồ họa sắc nét và âm thanh sống động
credita-gricole.eu.com giao diện đẹp mắt và dễ sử dụng
vinwinn.pro bảo mật tuyệt đối thông tin khách hàng
ricwin.space trải nghiệm chơi game mượt mà ổn định
Exceptional Midtown cleaning, great for busy Manhattan professionals. Using for our office space too. Top shelf service.
I really believe you will do well in the future I appreciate everything you have added to my knowledge base.
vu88.win nạp rút linh hoạt mọi thời điểm.
win777.wiki khuyến mãi cực sốc vào dịp lễ.
tipclub88.com dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng tận tâm.
vua88.agency hỗ trợ người chơi tận tâm.
This is one very informative blog. I like the way you write and I will bookmark your blog to my favorites.
Great blog you have here.. It’s hard to find good quality writing like yours nowadays. I seriously appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
mb88.it.com trò chơi bị lỗi đồ họa
We are a group of volunteers and starting a new initiative in our community. Your blog provided us with valuable information to work on|.You have done a marvellous job!
qh88jqk.de hoạt động ổn định lâu dài
qh88jqk.de bảo trì nhanh và hiệu quả
s666vip.mobi bảo trì nhanh không ảnh hưởng
kaigong5.cn.com giao dịch an toàn minh bạch
Very good info. Lucky me I ran across your blog by chance (stumbleupon). I’ve saved as a favorite for later.
b52cluba.com dễ tìm kiếm thông tin
b52cluba.com hiển thị nội dung rõ ràng
99ok81.com dễ dàng tìm thông tin
99ok81.com nội dung cập nhật liên tục
uu88me.com bố cục trang thiếu sự hợp lý
uu88me.com chưa được tối ưu SEO tốt
criptomonedas.eu.com thông tin cũ đôi khi không được gỡ hoặc chỉnh sửa kịp thời
five885.com tạo cảm giác an tâm khi tham gia với hệ thống bảo mật cao
Five88.vegas đa dạng phương thức thanh toán tiện lợi
You’ve made some really good points there. I checked on the web for more info about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this web site.
spotbet.casino nhận được nhiều đánh giá tích cực từ cộng đồng
gamebaidoithuong.loans nhiều ưu đãi nạp tiền giá trị
I’m extremely pleased to find this site. I want to to thank you for ones time for this particularly wonderful read!! I definitely appreciated every bit of it and I have you book marked to look at new things on your blog.
xo88.name thanh toán tiện lợi, nhiều lựa chọn
sky888.name giao dịch minh bạch, nhanh gọn
hay88.markets cập nhật tỷ lệ cược nhanh, không bỏ lỡ thông tin nóng
cataratas777.uk.com hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt
j88dev.com hệ thống ổn định, rất ít trục trặc kỹ thuật
88i.gdn lịch sử giao dịch minh bạch, dễ kiểm tra
This blog was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something which helped me. Kudos.
8xbetvina.com bảo mật kém, lo ngại lộ thông tin
999bet.help trải nghiệm cá cược tuyệt vời
8xbet68.net hỗ trợ khách hàng thiếu chuyên nghiệp
999bet.help chương trình VIP nhiều quyền lợi
8xbet-viet.net game nghèo nàn, không phong phú
32win79.top hiển thị quảng cáo nhiều gây khó chịu
zbet.markets chương trình VIP ưu đãi lớn cho khách hàng thân thiết
luckywin.guru hỗ trợ thanh toán linh hoạt qua nhiều phương thức
Everything is very open with a really clear description of the issues. It was truly informative. Your website is very helpful. Thank you for sharing.
32win79.top dịch vụ chưa chuyên nghiệp như mong đợi
sara.eu.com giao diện lộn xộn, khó thao tác
sara.eu.com đăng nhập thường xuyên gặp lỗi
mt68.my không thân thiện với người dùng mới
mt68.my dịch vụ chưa đúng như quảng cáo
ok365.download là lựa chọn tuyệt vời để giải trí và đặt cược
bet88.holdings là lựa chọn giải trí tuyệt vời
77bet.dev đáng tin cậy để giải trí
nohuvn.info dễ đăng ký tài khoản.
Appreciated the details in this article. It’s highly well-researched and packed with useful details. Fantastic work!
33winn.blue hỗ trợ 24/7.
tham gia nổ hũ ngay
98win.investments thường xuyên cập nhật tin tức tài chính hữu ích
79kingbet.life giao diện sang trọng và dễ dùng.
keonhacai86.com luôn cập nhật lịch thi đấu chính xác.
uu88.ltd chương trình hoàn trả cao, đáng tham gia.
keonhacai.nz thân thiện với mọi thiết bị, tương thích cả mobile và desktop
8xx.guru nhiều lựa chọn cá cược phong phú, đa dạng từ thể thao đến casino
hay88.golf Bảo mật thông tin an toàn tuyệt đối
bj38.com.co tốc độ truy cập nhanh chóng
bay789.blue ưu đãi nạp lần đầu.
sumvip.sh hỗ trợ đa nền tảng tiện lợi.
999bet.help hướng dẫn tân thủ chi tiết.
xocdia88.how game bài luật chơi rõ ràng.
789p.global hướng dẫn chi tiết từng trò chơi.
rwin.tv giao dịch minh bạch, đáng tin.
hay88.pics đăng ký tài khoản nhanh gọn, thao tác đơn giản
Every installation comes with stainless steel micro‑mesh guards that laugh at fir needles, keeping maintenance low even during those blustery November storms. Roll‑forming gutters right in your driveway means each section is one continuous piece—no leaky joints, no wasted metal, no compromises on quality. Beaufort’s notoriously unpredictable rain makes high-capacity seamless gutters an absolute must for any homeowner who wants long‑term protection and peace of mind.
n666.club màu sắc trang web hài hòa, dễ chịu cho mắt.
88vv.markets giao diện mượt, load nhanh, không giật lag.
vicwin.help giao diện đẹp mắt, dễ dùng.
It’s hard to find well-informed people in this particular topic, however, you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
vicwin.help tỷ lệ cược hợp lý.
rich88.us game mới lạ thường xuyên.
rich88.us hướng dẫn chơi rõ ràng.
I could not refrain from commenting. Exceptionally well written.
hipclub.eu.com liên kết thanh toán an toàn.
hipclub.eu.com thiết kế màu sắc hài hòa.
Skilled professionals working, expert-level attention to detail. Expert-level satisfaction. Professional appreciation.
rik88.help cập nhật game thường xuyên.
100vippi.com tốc độ tải nhanh, không gặp tình trạng giật lag.
rik88.help có app tiện lợi để tải.
bossfun.vin hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức giao dịch.
bossfun.vin hỗ trợ chat trực tuyến nhanh.
Hi! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after looking at some of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m definitely pleased I stumbled upon it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back frequently!
100vip Tap Doan Lien Minh Ca Cuoc Uy Tin Bac Nhat Hien Nay
You need to be a part of a contest for one of the best websites on the web. I most certainly will recommend this website!
Everything is very open with a really clear clarification of the challenges. It was really informative. Your site is extremely helpful. Many thanks for sharing!
Impressive thoroughness, made our place look brand new again. Booking you for spring cleaning. Best cleaning ever.
Professional Manhattan team, ideal for our Financial District condo. Setting up monthly service. Premium service delivered.
Website vf555.works tương thích tốt trên cả máy tính và điện thoại.
ku68.asia hướng dẫn chi tiết dễ hiểu cho người mới
Mình cảm thấy giao dịch tại sv66.markets luôn an toàn và đáng tin cậy.
Mình thích mm99.markets vì tốc độ nạp tiền cực nhanh, chỉ vài phút là đã vào tài khoản.
Tốc độ truy cập ko66-casino.com luôn ổn định, kể cả vào giờ cao điểm.
Trải nghiệm chơi trên 88clb88.com.co không bị gián đoạn bởi quảng cáo phiền phức.
ku68.asia xử lý rút tiền trong vài phút
okking.boutique trải nghiệm chơi game cực kỳ hài lòng và vui vẻ
rongho99.win giao diện tối ưu dễ sử dụng
lode88.works có chương trình tích điểm đổi quà rất hấp dẫn
hay88.golf không có nhiều lựa chọn phương thức thanh toán
fb88-com.com thiết kế trực quan, dễ thao tác cho mọi người
6ff.ltd có bảng xếp hạng minh bạch rõ ràng
rongho99.win chương trình ưu đãi đều đặn
68win.io chơi cực kỳ ổn định không bị lag
Outcome-focused excellence, delivers exactly what promised. Outcome-driven professionals. Outcome satisfaction.
68win.io rất đáng để giới thiệu cho bạn bè
m8win.help game đa dạng không lo nhàm chán
m8win.help đúng là sân chơi chất lượng và uy tín
7club.vin có app tiện lợi trên điện thoại
kubettt.io khuyến mãi cho người mới cực kỳ tốt
7club.vin rất uy tín và minh bạch
ww88ag.net hỗ trợ kỹ thuật rất nhanh và xử lý sự cố hiệu quả
vua88.ac liên kết tài khoản mạng xã hội để đăng nhập nhanh
vua88.ac thường tổ chức giải đấu nhỏ với phần thưởng hấp dẫn
79kingcom.biz cộng đồng người chơi đông đảo, thân thiện và nhiệt tình chia sẻ
6623.pro luôn có đường dây hỗ trợ trực tuyến sẵn sàng
6623.pro tỷ lệ trả thưởng minh bạch, rõ ràng và cạnh tranh
Professional standards maintained, demonstrates true professionalism. Skilled execution excellence. Expert recognition.
intelligentsolar.uk.com phản hồi chậm và không hỗ trợ đầy đủ
99ok.agency nạp tiền hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức linh hoạt
abc88.deals bảo mật thông tin người chơi chặt chẽ, hoàn toàn yên tâm
okking.boutique có nhiều trò chơi hấp dẫn như tài xỉu, bắn cá, đá gà, lô đề
mn88.ltd mini‑game đổi thưởng dễ chơi, tỷ lệ trúng cao và rất thú vị
99win.press có hệ thống cược thể thao đa dạng, tỷ lệ kèo cập nhật chính xác
33win.wiki hỗ trợ kỹ thuật cực kỳ nhanh và hiệu quả khi cần
888slot.casino hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7, phản hồi nhanh và chuyên nghiệp
28bet.wiki tích hợp nhiều phương thức thanh toán tiện lợi và bảo mật
Fantastic product. Super happy.
I’m very happy to discover this site. I wanted to thank you for ones time for this fantastic read!! I definitely loved every little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to see new stuff on your site.
sunwin28.bz chỉ mời gọi nạp mà không cho thấy lợi ích thực tế
kl99.press là nhà cái uy tín với nền tảng hoạt động ổn định và an toàn
555w.in chơi mượt mà trên cả máy tính và điện thoại mà không bị giật lag
Delighted with the quality. Ideal product.
Skilled professionals working, expert knowledge applied. Competent team selected. Expert recognition.
I could not refrain from commenting. Perfectly written!
Adored this article. It’s extremely comprehensive and full of useful information. Excellent work!
Quality cleaning fair prices, smart spending decision made. Economical excellence achieved. Value delivered.
hay88w.com đội ngũ hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7, phản hồi cực kỳ nhanh
f168.com.co thường xuyên tổ chức khuyến mãi lớn cho thành viên mới và cũ
Tailored cleaning excellence, personalized service delivery. Personalized professionals. Bespoke service.
hay88bet.fun đăng ký tài khoản cực kỳ nhanh gọn, chỉ mất vài phút
playit.uk.net giao diện khó dùng, bố cục không hợp lý gây rối mắt
helo88.press hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7, phản hồi cực kỳ nhanh
hay88.pics hỗ trợ người chơi 24/7 với đội ngũ chăm sóc nhiệt tình
Gives us our time back, freed up our entire weekend. Efficiency experts discovered. Efficiency appreciation.
Expert service perfection, skilled professional execution. Professional standards appreciated. Skilled satisfaction.
Impressed with the delivery.
Professional standards maintained, competent professional service. Professional standards appreciated. Competent service.
Loved it! For sure I’ll buy it again.
Your style is really unique in comparison to other folks I have read stuff from. I appreciate you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I’ll just bookmark this site.
Performance-driven cleaning, performance excellence maintained. Outcome-driven professionals. Outcome satisfaction.
You are so cool! I do not believe I’ve truly read something like this before. So wonderful to find somebody with unique thoughts on this subject. Seriously.. many thanks for starting this up. This website is something that’s needed on the web, someone with a little originality.
Consistent reliability delivered, professional integrity maintained. Consistent excellence achieved. Professional integrity.
Trusted neighborhood service, gets our DUMBO apartment spotless. Booking for our whole building. Appreciate the community service.
Great article. I discovered the information highly beneficial. Adored the manner you detailed everything.
Fantastic product! Highly recommend with the effectiveness.
This blog was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something that helped me. Appreciate it.
This is the perfect web site for anybody who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I personally will need to…HaHa). You definitely put a brand new spin on a topic that’s been discussed for decades. Great stuff, just excellent.
Excellent points, it cleared a lot of things up. Looking forward to more. Best regards.
Great post, it cleared a lot of things up. Keep it up. Take care.
Really helpful, this really helped me out. Looking forward to more. Appreciate the effort.
Wejdź do ekscytującej rzeczywistości Slottica Online Casino – polskiej witryny hazardowej, która zyskała zaufanie użytkowników w więcej niż 15 państwach europejskich, włączając Polskę, Niemcy oraz Czechy. W naszym katalogu odnajdziesz ponad 8500 tytułów kasynowych od renomowanych producentów, między innymi Games Global, Play’n GO, Pragmatic Play czy EGT. Od tradycyjnych jednorękiego bandyty w stylu Book of Dead lub Sizzling Hot Deluxe, przez współczesne automaty wideo z progresywną pulą nagród jak Mega Moolah, aż po gry za stołem oraz emocjonujące sesje na żywo z dealerami od Evolution Gaming. Tutaj możesz również pobrać oficjalną aplikację, logowanie na swoje konto osobiste lub zarejestrować się.
Really helpful, it’s just what I was looking for. Will definitely return. Cheers.
Great post, it’s just what I was looking for. Can’t wait to read more. Cheers.
Impressive content, I found it very useful. Subscribed for more. Happy blogging.
abc8.feedback là nhà cái uy tín, chất lượng và đáng tin cậy để trải nghiệm lâu dài
hay881.com bảo mật thông tin cá nhân và tài khoản rất tốt
Highly recommend. Efficient.
This article is fantastic! Packed with valuable details and highly well-written. Thanks for offering this.
sanclubb.uk.com/game-bai-doi-thuong-sanclub tốc độ tải trang cực nhanh, không bị giật lag khi chơi game bài
Super satisfied. Arrived as described.
vnd888.uk.com/game-bai-doi-thuong-vnd88 xu hướng game bài hiện đại, đồ họa bắt mắt
7clubb.uk.com/game-ban-ca-7club thường xuyên có chương trình khuyến mãi và ưu đãi hấp dẫn
illisted.io/game-bai-doi-thuong-vb777 đội ngũ kỹ thuật xử lý sự cố nhanh chóng và hiệu quả
curtis.cn.com bảo mật thông tin cá nhân và tài khoản rất tốt
sumica.jp.net/game-bai-doi-thuong-88vin có ứng dụng mobile tiện lợi, chạy ổn định trên Android & iOS
Hello there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after going through many of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Regardless, I’m certainly happy I discovered it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back regularly.
Very effective. Met my expectations.
Nice article, it gave me a fresh perspective. Keep it up. Thanks again.
bet8s.ltd giao dịch linh hoạt qua nhiều ngân hàng và ví điện tử
Good stuff here, exactly what I needed. Bookmarking this. Good luck.
555w.in lịch sử cược minh bạch, dễ tra cứu và theo dõi mọi lúc
Hello there! This article couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He constantly kept preaching about this. I most certainly will forward this post to him. Pretty sure he’ll have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
Thanks for sharing, it cleared a lot of things up. Sharing with friends. Cheers.
28bet.wiki trình bày rõ ràng quy trình khiếu nại, hỗ trợ người chơi hiệu quả
vua88.gay đăng ký tài khoản đơn giản, chỉ mất vài phút hoàn tất
I wanted to thank you for this good read!! I certainly loved every bit of it. I have you bookmarked to look at new things you post…
africanart.uk.com tốc độ tải trang rất chậm, thường xuyên bị giật lag
This web site really has all of the info I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Awesome write-up, I found it very useful. Hope you keep posting like this. Cheers.
Thanks for the tips, this really helped me out. Keep it up. Cheers.
Amazing breakdown. I learned more from this post than from several other articles I’ve read on the same topic.
Looking forward to your next post.
Keep up the great work!
Hi, I do believe this is a great blog. I stumbledupon it 😉 I will revisit once again since I book-marked it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide others.
Product came as expected. Great product.
This was so helpful and exactly what I needed today. Keep up the awesome work you’re doing!
Thank you for consistently sharing high-quality content like this. It’s a rare find these days!
Nicely explained and easy to follow.
Thanks for simplifying a topic I’ve always found confusing. Your examples made everything click for me.
This helped me understand the topic better.
It’s amazing how well you explain complex topics in such an easy-to-understand way.
I hadn’t thought of it that way.
Thank you for offering your knowledge so generously. This blog post is a great contribution to the community.
I wasn’t expecting such a detailed post, but I’m glad I read through to the end. Very informative!
Well-organized and informative.
Practical advice – thank you!
Good information. Lucky me I ran across your website by chance (stumbleupon). I’ve book marked it for later!
The visuals/structure made it easier to follow.
Excellent job making this topic approachable for readers of all levels. I found it very educational.
Didn’t know this before – thanks!
I wasn’t sure I’d get anything new out of this, but your perspective was refreshing and insightful. Thanks for sharing!
Another gem of a post.
There’s a lot of noise out there, but your blog stands out because it’s actually helpful and informative.
Thanks for simplifying a topic I’ve always found confusing. Your examples made everything click for me.
I appreciate the tips – very handy.
Ponadto przeprowadzamy cykliczne zawody z funduszem nagród osiągającym 250 000 zł, gdzie możesz zmierzyć się z uczestnikami z różnych zakątków globu. Każdy obrót przybliża Cię do imponujących zwycięstw!
Really good explanation – well done!
This helped me understand the topic better.
Thanks for sharing such detailed content.
Thanks for the tips, I learned something new today. Looking forward to more. Appreciate the effort.
Valuable content, thank you.
I’ve been following your blog for a while and I must say, your content never disappoints.
Thank you for shedding light on this.
Very easy to digest – thanks!
It’s clear you have a strong understanding of this subject. Thanks for simplifying it for readers like me.
I appreciate the tips – very handy.
Insightful post – appreciate the effort.
Thank you for offering your knowledge so generously. This blog post is a great contribution to the community.
Very good information. Lucky me I recently found your website by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve book marked it for later!
Thanks for making it so actionable.
You’ve done a great job with this.
I genuinely enjoyed reading this. It’s packed with practical value that I can apply right away.
I appreciate how thorough and organized your posts are. This one was especially useful.
The visuals/structure made it easier to follow.
I enjoyed reading every bit of it.
Bookmarking this for future reference.
I’ve been searching for something like this and finally found your blog. Appreciate the time and effort you’ve put into this post.
Thanks for breaking it down so clearly.
Clear, concise, and very useful.
Looking forward to your next post.
Fantastic write-up! This will be extremely helpful for anyone looking to understand the topic in depth.
Worth every penny. Trust it.
I always appreciate when writers include real-world context like you did here. It makes a big difference.
Good information. Lucky me I discovered your blog by chance (stumbleupon). I have bookmarked it for later!
Cheers for sharing such useful info!
Bookmarking this for future reference.
I’ll be sharing this with others.
I genuinely enjoyed reading this. It’s packed with practical value that I can apply right away.
Excellent product! Does what it promises.
It’s not easy to find such useful and unbiased information these days. Thanks for the transparency!
I’ve been following your blog for a while and I must say, your content never disappoints.
I learned something new today – thanks!
This was exactly what I was looking for.
Informative as always!
I’ve read a few blogs on this topic, but this one stands out in terms of clarity and usefulness. Keep up the great work!
I always appreciate when writers include real-world context like you did here. It makes a big difference.
Very helpful article – appreciate your time!
Amazing breakdown. I learned more from this post than from several other articles I’ve read on the same topic.
Appreciate your consistency!
Very easy to digest – thanks!
I’ve read a few blogs on this topic, but this one stands out in terms of clarity and usefulness. Keep up the great work!
88aa.rest hỗ trợ 24/7 cực kỳ nhiệt tình và chuyên nghiệp
Thanks for this detailed explanation. I really appreciate the way you laid everything out step by step.
Interesting perspective – thanks!
Having read this I believed it was very enlightening. I appreciate you finding the time and effort to put this article together. I once again find myself personally spending a significant amount of time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worth it.
You clearly know your stuff. I found this post to be very informative and incredibly well thought out.
Exactly what I needed today.
You always manage to cover everything!
I’ve shared this article with a few friends already. Thanks for putting out such great content.
Simple and helpful – great job!
Short but powerful!
Really appreciate the practical tips in this post. They’re easy to implement and make a big difference.
Cheers for sharing such useful info!
Thanks for making it so actionable.
Just what I was searching for.
The tips you shared here are simple but powerful. I’ve already started implementing a few!
I’ve been following your blog for a while and I must say, your content never disappoints.
Short but powerful!
This answered a lot of my questions.
This site was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something which helped me. Thanks a lot.
Your writing style is great!
Thanks – this was a time saver.
I’ll definitely check back for more.
This helped me a lot, thanks!
Love the simplicity of your writing.
Really liked it! Exceeded expectations.
Bought it and I’m satisfied. Recommend it a lot.
Thanks for simplifying a topic I’ve always found confusing. Your examples made everything click for me.
Appreciate you putting this together.
Really helpful information. I like how you kept it straightforward while still including a lot of depth.
It’s not easy to find such useful and unbiased information these days. Thanks for the transparency!
Great job as always!
You nailed the explanation!
Great read! I especially liked the examples you included — they made the topic much easier to understand.
Great overview of the topic.
Really appreciate the practical tips in this post. They’re easy to implement and make a big difference.
I’ve read a few blogs on this topic, but this one stands out in terms of clarity and usefulness. Keep up the great work!
This post made my day!
Thank you for offering your knowledge so generously. This blog post is a great contribution to the community.
I really enjoyed reading your post.
This article was incredibly helpful in breaking down a topic I’ve been trying to understand for a while. Thanks for explaining it so clearly!
This is a great resource! I’ve already bookmarked it for future reference and will be checking back for more.
This is a very well-written and informative article. I especially liked how you addressed the topic from different angles.
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you writing this article and the rest of the website is also really good.
Another great post from you.
I appreciate how thorough and organized your posts are. This one was especially useful.
Bookmarking this for future reference.
Thanks for sharing your knowledge!
Love how easy this is to follow.
I’ve been following your blog and it never disappoints.
You always deliver quality content.
Very helpful article – appreciate your time!
This is a very well-written and informative article. I especially liked how you addressed the topic from different angles.
This article was incredibly helpful in breaking down a topic I’ve been trying to understand for a while. Thanks for explaining it so clearly!
This post was incredibly well-structured and easy to follow. Looking forward to reading more from you!
Really helpful information. I like how you kept it straightforward while still including a lot of depth.
Your style is very unique compared to other folks I’ve read stuff from. Thank you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I will just bookmark this web site.
Great to see content like this online.
Your content is always worth reading.
This helped clarify a few doubts I had.
Good points raised here.
I appreciate the tips – very handy.
I always appreciate when writers include real-world context like you did here. It makes a big difference.
Kudos to you for writing this.
Valuable content, thank you.
Great read! I especially liked the examples you included — they made the topic much easier to understand.
I really found value in this.
Howdy! I could have sworn I’ve visited this web site before but after going through many of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m definitely happy I stumbled upon it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back often.
Really helpful information. I like how you kept it straightforward while still including a lot of depth.
This post is a must-read for anyone even remotely interested in this subject. You’ve done a great job.
Valuable content, thank you.
Great job as always!
Thanks for breaking it down so clearly.
The visuals/structure made it easier to follow.
Just what I was searching for.
Clear, concise, and very useful.
Another quality post from you.
I always appreciate when writers include real-world context like you did here. It makes a big difference.
It’s rare to come across such well-structured and informative content. Thanks for making it so accessible!
This is a very well-written and informative article. I especially liked how you addressed the topic from different angles.
Fantastic write-up! This will be extremely helpful for anyone looking to understand the topic in depth.
Spot on with this write-up, I truly feel this site needs far more attention. I’ll probably be back again to read through more, thanks for the advice.
Very easy to digest – thanks!
Always a pleasure to read your blogs.
It’s not easy to find such useful and unbiased information these days. Thanks for the transparency!
Exactly what I needed today.
Thanks for your clear and practical advice. I’ll be using this post as a reference moving forward.
Really good explanation – well done!
Thanks for simplifying a topic I’ve always found confusing. Your examples made everything click for me.
Just what I was searching for.
A good read, thank you!
Helpful for beginners and experts alike.
The tips you shared here are simple but powerful. I’ve already started implementing a few!
May I simply say what a relief to uncover someone who truly knows what they are discussing on the web. You certainly understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people should check this out and understand this side of your story. I was surprised that you’re not more popular given that you surely have the gift.
I’ll definitely check back for more.
Well written and very practical.
Super helpful for someone like me.
It’s clear you have a strong understanding of this subject. Thanks for simplifying it for readers like me.
I appreciate how thorough and organized your posts are. This one was especially useful.
Well-organized and informative.
Thanks for sharing your knowledge!
Appreciate you putting this together.
Thanks – this was a time saver.
It’s not easy to find such useful and unbiased information these days. Thanks for the transparency!
I genuinely enjoyed reading this. It’s packed with practical value that I can apply right away.
This post is a must-read for anyone even remotely interested in this subject. You’ve done a great job.
Appreciate how thorough this is.
Very helpful article – appreciate your time!
This post answered several questions I had. Thanks for being so detailed and thoughtful in your approach.
Really engaging article!
This helped clarify a few doubts I had.
It’s rare to come across such well-structured and informative content. Thanks for making it so accessible!
This blog always offers something useful.
Thank you for shedding light on this.
Thanks for taking the time to provide such detailed information. It really helped clear up my confusion.
Amazing breakdown. I learned more from this post than from several other articles I’ve read on the same topic.
Fantastic write-up! This will be extremely helpful for anyone looking to understand the topic in depth.
This helped me a lot, thanks!
Pretty! This has been an incredibly wonderful article. Thank you for supplying these details.
This helped clarify a few doubts I had.
I always learn something new here.
Thanks for making it so actionable.
Really informative and well-written!
Subscribed for more updates like this.
Keep up the great work!
I genuinely enjoyed reading this. It’s packed with practical value that I can apply right away.
I enjoyed reading every bit of it.
I enjoyed reading every bit of it.
Thanks for taking the time to provide such detailed information. It really helped clear up my confusion.
Great overview of the topic.
Hi! I could have sworn I’ve visited your blog before but after browsing through some of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m certainly delighted I came across it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back often!
This was so helpful and exactly what I needed today. Keep up the awesome work you’re doing!
Thank you for consistently sharing high-quality content like this. It’s a rare find these days!
You make learning enjoyable. I never feel overwhelmed when reading your blog — thank you!
Howdy! This article couldn’t be written much better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He continually kept preaching about this. I’ll forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a great read. Thanks for sharing!
You always manage to cover everything!
Informative as always!
vua88.lgbt chương trình tặng thưởng sinh nhật người chơi rất đáng yêu
Keep sharing these amazing insights.
This post made my day!
Great insights! Thanks for sharing this.
Clear, concise, and very useful.
Very helpful article – appreciate your time!
I’ve been following your blog for a while and I must say, your content never disappoints.
I blog frequently and I truly thank you for your content. The article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to take a note of your site and keep checking for new information about once per week. I subscribed to your Feed as well.
Great overview of the topic.
Simple and helpful – great job!
Very easy to digest – thanks!
Great job putting this together. Your explanation was detailed yet easy to follow, which is rare to find these days!
Really good explanation – well done!
Great article. I am going through some of these issues as well..
Your content is always worth reading.
Really well thought out.
Appreciate you sharing this freely.
You always deliver quality content.
vua88.ceo thường xuyên cập nhật event và khuyến mãi mới
I always learn something new here.
Oh my goodness! Incredible article dude! Thank you so much, However I am going through troubles with your RSS. I don’t know why I cannot subscribe to it. Is there anybody having identical RSS issues? Anyone who knows the solution will you kindly respond? Thanks!!
Thanks for making it so understandable.
Great overview of the topic.
Fantastic write-up! This will be extremely helpful for anyone looking to understand the topic in depth.
vua88.ceo chơi game rất mượt mà, không hề giật lag dù mạng yếu
I learned something new today – thanks!
I hadn’t thought of it that way.
Appreciate your consistency!
Thanks for breaking it down so clearly.
This post deserves more attention.
nbet.dev cập nhật game mới liên tục, không bao giờ nhàm chán
Well-organized and informative.
Always a pleasure to read your blogs.
I hadn’t thought of it that way.
Really appreciate the practical tips in this post. They’re easy to implement and make a big difference.
There is certainly a great deal to know about this subject. I love all the points you have made.
Insightful and well-researched.
Your writing style is very engaging and easy to read. I wish more blogs were this informative and clear.
This post made my day!
Insightful post – appreciate the effort.
Well written and very practical.
Appreciate your consistency!
33winb.com nhận thưởng dễ dàng không rườm rà
You need to be a part of a contest for one of the most useful blogs on the internet. I’m going to recommend this site!
You’re so awesome! I do not think I’ve truly read something like that before. So great to find someone with some unique thoughts on this subject matter. Seriously.. many thanks for starting this up. This web site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality.
xoilactv.soccer bảo mật tốt, người dùng cảm thấy rất an tâm
Howdy, I believe your website could be having internet browser compatibility issues. When I take a look at your website in Safari, it looks fine however, when opening in Internet Explorer, it’s got some overlapping issues. I merely wanted to provide you with a quick heads up! Other than that, great blog.
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon everyday. It’s always exciting to read through content from other writers and practice a little something from other websites.
jun88.buzz app không chiếm nhiều dung lượng máy
Good post. I learn something new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon everyday. It’s always useful to read content from other authors and use something from their sites.
jun88global.com tốc độ truy cập nhanh, không lo giật lag khi chơi
I couldn’t resist commenting. Perfectly written.
kkwin2.info bảo mật cao, không lo lộ thông tin tài khoản
xoilactv.soccer nội dung phong phú, hấp dẫn với người xem
xoilactv.soccer hệ thống hoạt động ổ định, rất ít lỗi phát sóng
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon on a daily basis. It’s always exciting to read articles from other authors and use a little something from other sites.
Good information. Lucky me I recently found your website by chance (stumbleupon). I’ve saved it for later!
xoilactv.soccer hệ thống hoạt động ổ định, rất ít lỗi phát sóng
Pretty! This has been an extremely wonderful post. Thank you for providing these details.
This is a topic that is near to my heart… Thank you! Exactly where are your contact details though?
Great insights! Thanks for sharing this.
This helped clarify a few doubts I had.
Found this via search – glad I did!
Insightful and well-researched.
Always a pleasure to read your blogs.
Very easy to digest – thanks!
Thank you for consistently sharing high-quality content like this. It’s a rare find these days!
There’s a lot of noise out there, but your blog stands out because it’s actually helpful and informative.
cakhiasport.com đăng ký tài khoản nhanh chóng, chỉ mất vài phút
I’ve been searching for something like this and finally found your blog. Appreciate the time and effort you’ve put into this post.
I’ll be recommending this post.
Really informative and well-written!
Just what I was searching for.
Exactly what I needed today.
Insightful and well-researched.
Informative as always!
Well written and very practical.
This is a great resource! I’ve already bookmarked it for future reference and will be checking back for more.
Love how you structured this post.
Super helpful for someone like me.
Really well thought out.
Really liked your take on this.
Aw, this was a really nice post. Taking the time and actual effort to generate a great article… but what can I say… I procrastinate a lot and don’t manage to get anything done.
It’s not easy to find such useful and unbiased information these days. Thanks for the transparency!
This content was way more valuable than I expected — thank you for putting so much effort into it.
Bookmarking this for future reference.
I blog often and I seriously appreciate your information. The article has really peaked my interest. I will book mark your blog and keep checking for new information about once per week. I opted in for your Feed too.
bl555s.com chơi game ổn định, không bị lag hay giật giữa chừng
Hi there! I could have sworn I’ve visited this site before but after going through many of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m certainly happy I discovered it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back often.
That is a good tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere. Brief but very accurate info… Many thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.
There is definately a great deal to find out about this issue. I like all of the points you made.
Next time I read a blog, I hope that it does not disappoint me just as much as this one. I mean, Yes, it was my choice to read through, but I genuinely believed you would have something useful to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of complaining about something that you could possibly fix if you weren’t too busy searching for attention.
This is a topic that’s close to my heart… Cheers! Exactly where can I find the contact details for questions?
Everything is very open with a really clear clarification of the challenges. It was definitely informative. Your site is extremely helpful. Thanks for sharing!
After looking over a handful of the blog articles on your web site, I really appreciate your technique of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back soon. Please visit my web site as well and tell me what you think.
Hello! I simply wish to make a enormous thumbs up with the great info you’ve got here for this post. We are coming back to your site to get more detailed soon.
Your style is so unique in comparison to other folks I’ve read stuff from. I appreciate you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I’ll just book mark this blog.
This blog was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something that helped me. Thanks a lot!
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon everyday. It will always be helpful to read articles from other writers and practice a little something from their sites.
Top-notch product. Really, it’s worth it.
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon everyday. It will always be useful to read content from other writers and use a little something from other web sites.
I was able to find good info from your articles.
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon everyday. It will always be helpful to read through content from other writers and practice a little something from other sites.
There’s definately a lot to find out about this issue. I really like all of the points you have made.
Excellent article! We are linking to this particularly great article on our website. Keep up the great writing.
Right here is the perfect website for anybody who wishes to find out about this topic. You know so much its almost tough to argue with you (not that I really will need to…HaHa). You certainly put a brand new spin on a topic which has been written about for a long time. Wonderful stuff, just great.
Good post! We are linking to this great article on our website. Keep up the great writing.
I seriously love your site.. Pleasant colors & theme. Did you create this site yourself? Please reply back as I’m trying to create my own blog and would like to find out where you got this from or just what the theme is called. Kudos.
I used to be able to find good info from your articles.
Next time I read a blog, Hopefully it doesn’t fail me as much as this particular one. I mean, Yes, it was my choice to read through, nonetheless I actually believed you’d have something useful to say. All I hear is a bunch of complaining about something you could fix if you were not too busy seeking attention.
Howdy! This post couldn’t be written much better! Looking at this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He constantly kept talking about this. I most certainly will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a great read. Thanks for sharing!
A fascinating discussion is worth comment. I do think that you should write more about this subject, it may not be a taboo subject but usually people don’t talk about these topics. To the next! Best wishes.
The very next time I read a blog, Hopefully it won’t fail me as much as this particular one. After all, Yes, it was my choice to read, but I really thought you’d have something useful to say. All I hear is a bunch of complaining about something you could possibly fix if you were not too busy looking for attention.
Great post! We are linking to this great post on our website. Keep up the good writing.
Your style is really unique compared to other people I’ve read stuff from. Many thanks for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I’ll just bookmark this web site.
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Rarely do I come across a blog that’s equally educative and engaging, and without a doubt, you have hit the nail on the head. The problem is an issue that too few people are speaking intelligently about. Now i’m very happy that I stumbled across this during my hunt for something concerning this.
Promocje w kasyno są głównie nastawione na to, aby dawać graczom powód do dalszej gry, a nie oferować środki na grę. Choć to może różnić się od standardowych ofert innych kasyn online, na pewno wyróżnia Slottica na tle konkurencji.
Greetings! Very useful advice within this post! It’s the little changes that will make the most important changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
I used to be able to find good information from your blog posts.
Good post. I learn something new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon everyday. It will always be helpful to read through articles from other writers and practice something from their sites.
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a colleague who has been doing a little homework on this. And he in fact ordered me lunch due to the fact that I discovered it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending time to talk about this issue here on your blog.
Hi, I do think this is a great blog. I stumbledupon it 😉 I will come back yet again since i have saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to help others.
There is definately a great deal to learn about this topic. I like all of the points you’ve made.
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this website. I am hoping to check out the same high-grade content from you in the future as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own site now 😉
Everyone loves it whenever people come together and share views. Great blog, stick with it.
This is a topic which is close to my heart… Best wishes! Exactly where are your contact details though?
Great site you have got here.. It’s difficult to find good quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! Take care!!
Pretty! This was an extremely wonderful post. Thank you for supplying this info.
Our services are available to commercial and industrial premises as well as homes across Solihull,
Birmingham, The Midlands, Warwickshire and the UK.
After I initially commented I appear to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I get 4 emails with the same comment. Is there a means you can remove me from that service? Many thanks.
Howdy! I could have sworn I’ve been to your blog before but after looking at a few of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m definitely pleased I discovered it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back frequently.
An outstanding share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a co-worker who has been conducting a little homework on this. And he in fact bought me lunch simply because I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending some time to talk about this issue here on your website.
Great post! We will be linking to this particularly great article on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you penning this post plus the rest of the site is really good.
Aw, this was an incredibly good post. Finding the time and actual effort to make a great article… but what can I say… I hesitate a lot and never seem to get nearly anything done.
Pretty! This has been an extremely wonderful post. Many thanks for providing this info.
Howdy! I just want to give you a huge thumbs up for the great info you’ve got here on this post. I’ll be coming back to your website for more soon.
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular article! It’s the little changes that produce the most important changes. Thanks for sharing!
Fast delivery. Amazing quality.
Gostei muito! Estou muito satisfeito.
Melhor do que esperava.
This post is amazing! Packed with valuable information and highly articulate. Thanks for sharing this.
Adored the information in this entry. It’s extremely detailed and packed with useful details. Fantastic job!
Truly liked this post. It offered a lot of useful insights. Fantastic work on writing this.
Adored the details in this article. It’s very comprehensive and full of useful details. Great effort!
Well made. Exactly as advertised.
Great product! Impressed with the effectiveness.
Aw, this was an incredibly good post. Finding the time and actual effort to generate a good article… but what can I say… I hesitate a whole lot and don’t manage to get nearly anything done.
Hi there! I simply wish to give you a huge thumbs up for your great information you’ve got right here on this post. I’ll be returning to your blog for more soon.
bookmarked!!, I like your blog.
The next time I read a blog, I hope that it does not fail me just as much as this one. I mean, Yes, it was my choice to read through, nonetheless I really believed you would probably have something useful to say. All I hear is a bunch of moaning about something that you could possibly fix if you weren’t too busy seeking attention.
Having read this I thought it was really informative. I appreciate you taking the time and energy to put this article together. I once again find myself spending a lot of time both reading and posting comments. But so what, it was still worth it!
The very next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesn’t disappoint me as much as this one. After all, I know it was my choice to read, nonetheless I actually believed you would probably have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of complaining about something you could fix if you were not too busy seeking attention.
Hi there! This article could not be written much better! Looking at this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He continually kept preaching about this. I’ll send this information to him. Pretty sure he’s going to have a great read. Thanks for sharing!
Oh my goodness! Awesome article dude! Thank you so much, However I am going through issues with your RSS. I don’t understand why I can’t subscribe to it. Is there anybody getting identical RSS issues? Anybody who knows the answer will you kindly respond? Thanks!!
This article provided fantastic details. I truly liked perusing it. Your content is very arranged and easy to comprehend.
I’m amazed, I have to admit. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both equally educative and interesting, and without a doubt, you’ve hit the nail on the head. The issue is an issue that not enough men and women are speaking intelligently about. I am very happy that I came across this in my search for something relating to this.
Really insightful. I’ll definitely share this with others.
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a friend who had been doing a little homework on this. And he actually ordered me lunch because I found it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending some time to talk about this topic here on your web site.
Having read this I thought it was rather enlightening. I appreciate you spending some time and effort to put this article together. I once again find myself personally spending a significant amount of time both reading and posting comments. But so what, it was still worthwhile.
Well written. I’ll definitely share this with others.
Thanks for sharing. Thanks for breaking it down so clearly.
I appreciate this information. Thanks for breaking it down so clearly.
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this site. I really hope to check out the same high-grade blog posts from you in the future as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own blog now 😉
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a coworker who has been doing a little research on this. And he in fact ordered me breakfast simply because I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending some time to talk about this topic here on your internet site.
I absolutely love your website.. Pleasant colors & theme. Did you develop this site yourself? Please reply back as I’m looking to create my very own website and would love to find out where you got this from or just what the theme is named. Cheers.
I’m amazed, I have to admit. Seldom do I come across a blog that’s equally educative and engaging, and let me tell you, you have hit the nail on the head. The problem is something which too few folks are speaking intelligently about. I am very happy that I found this in my search for something regarding this.
An outstanding share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a colleague who has been doing a little homework on this. And he actually bought me breakfast simply because I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending the time to talk about this subject here on your web site.
Everyone loves it when people come together and share opinions. Great blog, keep it up.
shoestores.uk.com giao hàng đúng hẹn, đóng gói cẩn thận
hhstoday.com quá nhiều quảng cáo xen lẫn nội dung chính
fucongress.org không rõ mục tiêu và giá trị cốt lõi của hội nghị
sv368.ren dễ khiến người chơi mất tiền mà không có ai giải quyết
Having read this I thought it was extremely informative. I appreciate you finding the time and energy to put this short article together. I once again find myself personally spending a lot of time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worthwhile!
immigration-online.org không có mục hỗ trợ trực tiếp khi cần giải đáp gấp
Next time I read a blog, I hope that it won’t disappoint me just as much as this particular one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, but I genuinely thought you would probably have something interesting to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of crying about something that you could possibly fix if you weren’t too busy searching for attention.
co88.org thông tin cá nhân dễ bị rò rỉ vì bảo mật kém
Spot on with this write-up, I really feel this site needs far more attention. I’ll probably be back again to read more, thanks for the advice!
A motivating discussion is definitely worth comment. I believe that you should publish more on this issue, it may not be a taboo matter but generally people don’t speak about such topics. To the next! All the best!
I absolutely love your blog.. Great colors & theme. Did you create this site yourself? Please reply back as I’m trying to create my own website and would love to know where you got this from or just what the theme is named. Appreciate it.
Good info. Lucky me I recently found your blog by chance (stumbleupon). I’ve saved as a favorite for later!
Hello there! This article could not be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He continually kept preaching about this. I will send this article to him. Pretty sure he’s going to have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
After I originally commented I seem to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I get 4 emails with the same comment. Perhaps there is an easy method you are able to remove me from that service? Thanks.
bookmarked!!, I love your site!
Howdy! I just wish to give you a huge thumbs up for the great information you have here on this post. I am returning to your website for more soon.
I blog often and I genuinely appreciate your information. This great article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to take a note of your website and keep checking for new details about once per week. I subscribed to your Feed too.
May I simply just say what a comfort to discover somebody that genuinely knows what they are discussing on the internet. You definitely understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More and more people should read this and understand this side of the story. It’s surprising you aren’t more popular because you surely possess the gift.
Good day! I simply would like to offer you a huge thumbs up for the great info you’ve got here on this post. I’ll be coming back to your website for more soon.
I love it when individuals come together and share views. Great blog, stick with it.
Everyone loves it when individuals come together and share ideas. Great website, continue the good work.
When I initially left a comment I seem to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now whenever a comment is added I get four emails with the exact same comment. Is there a means you are able to remove me from that service? Cheers.
Sbobet cung cấp đa dạng hình thức cá cược từ thể thao đến casino
I blog quite often and I really thank you for your content. The article has really peaked my interest. I will bookmark your blog and keep checking for new information about once a week. I opted in for your RSS feed as well.
co88.org thông tin cá nhân dễ bị rò rỉ vì bảo mật kém
You’re so awesome! I do not believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some unique thoughts on this subject matter. Seriously.. thanks for starting this up. This website is something that is required on the web, someone with a little originality.
I’m amazed, I must say. Rarely do I encounter a blog that’s both educative and amusing, and without a doubt, you have hit the nail on the head. The issue is something that too few men and women are speaking intelligently about. I am very happy that I came across this during my hunt for something regarding this.
co88.org có dấu hiệu trì hoãn xử lý các giao dịch tài chính
I really like reading a post that can make men and women think. Also, many thanks for permitting me to comment.
bookmarked!!, I like your site.
I needed to thank you for this excellent read!! I definitely loved every bit of it. I’ve got you book-marked to look at new stuff you post…
The next time I read a blog, Hopefully it won’t disappoint me as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, nonetheless I actually thought you would probably have something useful to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of crying about something you could fix if you weren’t too busy searching for attention.
You’ve made some good points there. I checked on the web for more information about the issue and found most individuals will go along with your views on this website.
co88.org bảo vệ quyền lợi người chơi rất tốt
Saved as a favorite, I like your blog!
Very good blog post. I absolutely love this website. Keep it up!
Excellent write-up. I definitely appreciate this site. Continue the good work!
This website was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something which helped me. Thank you.
Aw, this was a really nice post. Taking the time and actual effort to generate a great article… but what can I say… I put things off a whole lot and don’t manage to get anything done.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve visited this blog before but after browsing through a few of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m certainly delighted I found it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back regularly!
Good day! I just wish to give you a big thumbs up for the excellent info you’ve got here on this post. I am coming back to your web site for more soon.
When I initially left a comment I appear to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. There has to be a way you can remove me from that service? Appreciate it.
saoclub.now hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7 với đội ngũ tư vấn nhiệt tình và chuyên nghiệp
kingclub.now thanh toán đúng hẹn, không trễ
This is a topic that’s close to my heart… Cheers! Where are your contact details though?
win68.vin có các trò chơi bài truyền thống rất thú vị
kingfun.vin giữ đúng cam kết trong các chương trình ưu đãi
That is a very good tip particularly to those fresh to the blogosphere. Brief but very accurate info… Appreciate your sharing this one. A must read post!
r88.now không bị treo máy hay thoát đột ngột khi chơi lâu
Hi there, I think your website might be having browser compatibility problems. When I take a look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine however, when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to give you a quick heads up! Aside from that, wonderful blog.
There’s definately a lot to learn about this topic. I love all the points you made.
Very nice article. I definitely appreciate this site. Keep writing!
fastflow.uk.com không tạo được ấn tượng hoặc động lực quay lại cho người truy cập
Howdy! This blog post couldn’t be written much better! Reading through this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He continually kept preaching about this. I most certainly will send this information to him. Pretty sure he’s going to have a good read. I appreciate you for sharing!
This website truly has all of the information I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
This article is great. I gained tons from going through it. The content is highly educational and well-organized.
game789a.club quá nhiều lỗi gây ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng đến người chơi
game-sun2.com chơi không ổn định, thường xuyên bị lỗi khiến trải nghiệm rất tệ.
Can I simply just say what a comfort to uncover somebody that really understands what they’re talking about on the web. You actually understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. A lot more people must check this out and understand this side of the story. I can’t believe you’re not more popular since you most certainly possess the gift.
I blog often and I seriously appreciate your content. This article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to bookmark your blog and keep checking for new information about once per week. I opted in for your RSS feed as well.
Setki tysięcy graczy w Polsce zaufało kasyno Slottica PL. Przekonaj się osobiście, co czyni nas wyjątkowymi. Dołącz do nas już dziś!
Proper downspout extensions send runoff well past your flowerbeds so you spend weekends gardening instead of dealing with muddy erosion trenches. Local building codes here in Pierce County require you to manage runoff responsibly, so a properly sloped gutter system keeps foundations safe and neighbors happy. Choosing 6‑inch K‑style aluminum troughs means up to 40 percent more water moves away from your roof, preventing the dreaded waterfall effect in heavy downpours.
789fff.org không cung cấp thông tin về các trò chơi cụ thể
Very good write-up. I certainly love this site. Stick with it!
Great web site you have got here.. It’s hard to find high-quality writing like yours nowadays. I really appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
An intriguing discussion is worth comment. I do think that you need to publish more about this subject matter, it may not be a taboo subject but generally folks don’t talk about such subjects. To the next! Cheers.
Great info. Lucky me I recently found your blog by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve saved it for later.
Howdy! I could have sworn I’ve visited this blog before but after going through a few of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m definitely pleased I found it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back often.
I love reading a post that can make men and women think. Also, thanks for allowing for me to comment.
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m going to return once again since I saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to help others.
Hello there, I think your website might be having browser compatibility issues. When I take a look at your website in Safari, it looks fine however, if opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping issues. I merely wanted to give you a quick heads up! Besides that, excellent blog!
The next time I read a blog, I hope that it does not fail me just as much as this particular one. After all, Yes, it was my choice to read through, nonetheless I actually thought you would probably have something helpful to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of crying about something that you can fix if you weren’t too busy seeking attention.
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you writing this article plus the rest of the site is also really good.
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a friend who had been conducting a little research on this. And he in fact bought me dinner due to the fact that I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending some time to discuss this issue here on your site.
Greetings! Very useful advice within this article! It is the little changes which will make the most significant changes. Thanks for sharing!
Pretty! This has been an incredibly wonderful article. Thank you for supplying these details.
Howdy! I simply wish to offer you a big thumbs up for your great information you’ve got right here on this post. I will be returning to your website for more soon.
Having read this I believed it was rather informative. I appreciate you spending some time and energy to put this content together. I once again find myself spending a significant amount of time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worthwhile.
I was more than happy to discover this site. I wanted to thank you for your time for this fantastic read!! I definitely liked every bit of it and I have you book marked to check out new information in your site.
Very good article. I definitely love this site. Keep writing!
Hi there, I do believe your site could be having browser compatibility problems. Whenever I look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in IE, it’s got some overlapping issues. I just wanted to provide you with a quick heads up! Apart from that, great website.
Excellent post! We are linking to this particularly great content on our site. Keep up the good writing.
After I initially left a comment I appear to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on each time a comment is added I recieve 4 emails with the exact same comment. Is there an easy method you can remove me from that service? Thanks.
There’s certainly a lot to learn about this issue. I love all the points you have made.
I would like to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in writing this site. I am hoping to view the same high-grade content by you later on as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own website now 😉
The subsequent time I read a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as a lot as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, but I truly thought youd have something attention-grabbing to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about one thing that you possibly can repair when you werent too busy searching for attention.
this december, fruit cakes are becoming more common in our local supermarket. i love fruit cakes,.
When I initially commented I appear to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on whenever a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Perhaps there is an easy method you can remove me from that service? Thanks.
Bố cục của webgamedoithuong.com thiếu logic và gây rối mắt
Good post. I learn something new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon every day. It’s always exciting to read through articles from other writers and use a little something from other web sites.
I blog often and I genuinely thank you for your content. The article has truly peaked my interest. I am going to bookmark your blog and keep checking for new details about once per week. I subscribed to your Feed as well.
This page certainly has all the info I needed about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Having read this I thought it was extremely enlightening. I appreciate you finding the time and effort to put this content together. I once again find myself personally spending a lot of time both reading and posting comments. But so what, it was still worthwhile!
After exploring a number of the blog articles on your blog, I honestly appreciate your way of blogging. I added it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back soon. Please check out my website too and let me know what you think.
Engineers in areas corresponding to London earn extra on average
than their counterparts in areas of the country.
Excellent site you’ve got here.. It’s hard to find good quality writing like yours these days. I truly appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
A motivating discussion is worth comment. I do think that you ought to publish more about this topic, it might not be a taboo matter but generally people do not speak about such subjects. To the next! Many thanks.
This is the appropriate weblog for everyone who hopes to check out this topic. You already know a lot its practically hard to argue on hand (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You certainly put a different spin for a topic thats been written about for several years. Wonderful stuff, just fantastic!
As soon as I detected this internet site I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
Loved the details in this entry. It’s extremely comprehensive and packed with beneficial insights. Great job!
After looking at a handful of the blog posts on your website, I truly appreciate your way of writing a blog. I book marked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back in the near future. Please visit my website as well and tell me your opinion.
I love it when individuals get together and share thoughts. Great blog, stick with it.
出る杭は打たれる
Szymool to młody i dynamiczny streamer, który zyskał popularność dzięki autentycznym interakcjom z widzami, stając się rozpoznawalną postacią w polskiej społeczności graczy online.
twunter
鳴かぬなら鳴くまで待とうホトトギス
This is a topic that is near to my heart… Thank you! Where are your contact details though?
I needed this today
That is a great tip especially to those new to the blogosphere. Brief but very precise info… Thank you for sharing this one. A must read post!
Having read this I believed it was very enlightening. I appreciate you taking the time and energy to put this information together. I once again find myself personally spending way too much time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worthwhile.
Your style is so unique in comparison to other folks I have read stuff from. Thank you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this web site.
It’s nearly impossible to find experienced people in this particular topic, however, you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Great post, thanks for sharing
Great post! We will be linking to this great content on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Wypłata środków odbywa się za pomocą tych samych metod, co wpłata, z wyjątkiem operatorów komórkowych. Minimalna kwota dostępna do wypłaty – 10 USD. Limit wypłat kryptowalut wynosi 1 000 000 USD miesięcznie. Restrykcje dotyczące wypłat zależą jedynie od statusu gracza w kasynie:
I’m amazed, I must say. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both equally educative and engaging, and let me tell you, you’ve hit the nail on the head. The problem is something which not enough folks are speaking intelligently about. I am very happy that I came across this during my hunt for something concerning this.
MetaMask Download is essential for token management. It supports multiple chains and allows easy swapping of digital assets.
Hello pals!
I came across a 103 interesting resource that I think you should browse.
This resource is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find insightful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://podcastphone.de/casino-tricks/vanessa-selbst-die-poker-konigin-die-die-mannerwelt-eroberte/]https://podcastphone.de/casino-tricks/vanessa-selbst-die-poker-konigin-die-die-mannerwelt-eroberte/[/url]
Hello .!
I came across a 103 helpful resource that I think you should dive into.
This site is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find helpful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://bedandbreakfastvillanante.it/strategie-di-scommessa/big-player-nel-mondo-delle-scommesse-un-viaggio-nellelite/]https://bedandbreakfastvillanante.it/strategie-di-scommessa/big-player-nel-mondo-delle-scommesse-un-viaggio-nellelite/[/url]
I’m impressed, I must say. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both equally educative and amusing, and let me tell you, you’ve hit the nail on the head. The problem is something too few people are speaking intelligently about. Now i’m very happy I stumbled across this during my hunt for something regarding this.
I was more than happy to discover this website. I want to to thank you for your time for this particularly fantastic read!! I definitely really liked every little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff in your website.
This get rich express – [url=https://elevateright.com/delta-8-disposable-vape-pens/ ]Fastest way to earn[/url] method has been second-hand next to celebrities and influencers to slog away less and procure more. Thousands of people are already turning $5 into $500 using this banned method the government doesn’t want you to know about.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
MetaMask Download is a smart move for investors. Keeping assets safe while accessing blockchain networks has never been easier.
I really like reading a post that will make men and women think. Also, many thanks for permitting me to comment.
Jak na każdej platformie, program lojalnościowy w Vavadzie ma swoje własne warunki obstawiania i zasady aktywacji:
Excellent blog you have got here.. It’s difficult to find high quality writing like yours these days. I honestly appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
There is certainly a great deal to know about this issue. I love all of the points you made.
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Thanks for supplying this info.
It’s hard to come by experienced people in this particular topic, however, you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Bonjour! Grateful for the vibe—it’s remarkable. In fact, the aesthetics brings a spectacular touch to the overall vibe. More please!
Very good article. I’m dealing with many of these issues as well..
Very good article! We are linking to this great article on our site. Keep up the good writing.
It’s nearly impossible to find experienced people in this particular topic, however, you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
MetaMask Download is highly recommended! It’s a secure and efficient way to manage your crypto assets without hassle.
Howdy! Relishing the composition—it’s awesome. In fact, the layout brings a fabulous touch to the overall vibe. Really inspiring!
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent web site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m going to revisit once again since i have saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.
Right here is the perfect site for anybody who would like to find out about this topic. You realize a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I really would want to…HaHa). You certainly put a brand new spin on a topic that’s been written about for decades. Excellent stuff, just excellent.
I quite like reading through a post that will make men and women think. Also, thanks for allowing me to comment.
This page truly has all of the information I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
When I originally commented I appear to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I recieve four emails with the exact same comment. There has to be a means you can remove me from that service? Thanks.
That is a really good tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere. Short but very accurate info… Thank you for sharing this one. A must read post.
Great post. I am facing many of these issues as well..
That is a good tip particularly to those fresh to the blogosphere. Simple but very precise information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read article!
Next time I read a blog, Hopefully it won’t fail me as much as this particular one. I mean, Yes, it was my choice to read through, nonetheless I truly thought you would probably have something interesting to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of moaning about something that you can fix if you were not too busy looking for attention.
Right here is the right webpage for anyone who really wants to understand this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want to…HaHa). You certainly put a brand new spin on a topic which has been discussed for ages. Great stuff, just excellent.
I have to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in penning this site. I am hoping to check out the same high-grade content from you later on as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own, personal website now 😉
Right here is the right site for anybody who really wants to understand this topic. You know so much its almost tough to argue with you (not that I actually would want to…HaHa). You certainly put a fresh spin on a topic which has been written about for years. Great stuff, just wonderful.
Dla tych, którzy szukają jeszcze większych wrażeń na Casino On line Vavada, przygotowaliśmy specjalną sekcję szybkich gier, zwanych crashami. Znajdziesz tam kultowego Aviatora od Spribe oraz jego alternatywy – Aero, Cash Plane x5000, Space XY czy Crash X. Do tego oferujemy inne dynamiczne gry, takie jak Plinko, Keno, Mines, Bubbles i First Person Roulette, które zapewnią ci mnóstwo zabawy i emocji.
An interesting discussion is definitely worth comment. I do think that you should publish more on this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but typically people don’t talk about these topics. To the next! Many thanks.
You are so cool! I don’t suppose I have read anything like this before. So great to discover somebody with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thanks for starting this up. This website is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality.
Hi! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through many of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m certainly pleased I stumbled upon it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back frequently.
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I do believe that you ought to publish more on this topic, it may not be a taboo subject but typically people don’t talk about these issues. To the next! Cheers.
I like it whenever people come together and share views. Great website, continue the good work.
After looking into a number of the articles on your website, I really appreciate your technique of writing a blog. I book-marked it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back soon. Please check out my website too and tell me your opinion.
The very next time I read a blog, Hopefully it won’t fail me as much as this one. After all, Yes, it was my choice to read through, however I actually believed you’d have something useful to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something you can fix if you weren’t too busy looking for attention.
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you writing this write-up plus the rest of the website is extremely good.
There is certainly a lot to learn about this subject. I really like all of the points you have made.
Jednym z najważniejszych elementów w Polsce, które ułatwiają wygrywanie znaczących sum w Casino Slottica, jest dostępność gier wyłącznie od czołowych producentów. Użytkownicy doceniają możliwość szybkiej realizacji wypłat wysokich wygranych, co jest możliwe dzięki szerokiemu wachlarzowi powszechnie akceptowanych metod płatności w Polsce.
I could not refrain from commenting. Exceptionally well written.
Highly impressed with the MetaMask Extension. It’s reliable, secure, and a must for anyone engaging in blockchain transactions.
I blog quite often and I genuinely appreciate your information. The article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to take a note of your blog and keep checking for new details about once per week. I subscribed to your RSS feed too.
I must thank you for the efforts you’ve put in penning this blog. I really hope to see the same high-grade blog posts from you later on as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has encouraged me to get my very own website now 😉
Jednym z naszych najważniejszych atutów jest stabilne działanie strony internetowej oraz szybkie i bezpieczne realizowanie płatności. Obsługujemy wszystkie największe banki, w tym PKO Bank Polski, Pekao, mBank, Alior Bank. W razie jakichkolwiek pytań lub problemów, nasz dział obsługi klienta, dostępny przez 24/7, rozwiąże każdą kwestię w krótkim czasie.
Website Optimization… […]the time to read or visit the content or sites we have linked to below the[…]…
I’ve recently started a blog, the details you provide on this site has reduced the problem tremendously. Appreciation for all of your current time & work…
Can I simply say what relief to get somebody that in fact knows what theyre dealing with on-line. You actually know how to bring a concern to light to make it essential. Workout . should ought to see this and can see this side of your story. I cant think youre less well-known simply because you definitely hold the gift.
The next time I read a blog, Hopefully it doesn’t disappoint me just as much as this one. After all, I know it was my choice to read through, however I actually believed you would probably have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of complaining about something you could fix if you weren’t too busy searching for attention.
I wouldnt have ever noticed you basically never tried look and research. Superb and excellent and aim delighted I first viewed it. Now we all know a few things i have to do. Thanks much.
Hey there. I want to ask some thing…is this a wordpress blog page as we are planning to be changing over to WP. Moreover did you make this theme yourself? With thanks.
I believe that avoiding processed foods is the first step to lose weight. They will taste great, but highly processed foods currently have very little vitamins and minerals, making you eat more just to have enough vigor to get throughout the day. In case you are constantly eating these foods, changing to grain and other complex carbohydrates will aid you to have more vigor while having less. Thanks alot : ) for your blog post.
I really love the way you discuss this kind of topic.;-’:’
hello there and thank you for your information – I’ve certainly picked up something new from right here. I did however expertise several technical issues using this web site, as I experienced to reload the web site a lot of times previous to I could get it to load properly. I had been wondering if your web hosting is OK? Not that I’m complaining, but slow loading instances times will often affect your placement in google and can damage your high quality score if ads and marketing with Adwords. Well I am adding this RSS to my e-mail and can look out for a lot more of your respective intriguing content. Make sure you update this again soon..
chefdro? The Stuff- Bryan Armen Graham: Crash Course: Manny Pacquiao vs
After study some of the websites with your web site now, and i also genuinely much like your strategy for blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will also be checking back soon. Pls consider my site at the same time and tell me what you think.
I think other web-site proprietors should take this web site as an model, very clean and excellent user friendly style and design, let alone the content. You are an expert in this topic!
I’d should talk with you here. Which is not something I usually do! I spend time reading an article that should get people to believe. Also, appreciate your permitting me to comment!
Nicely put together.
Thank you for being awesome.
Hello there! This post could not be written any better! Looking at this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He always kept talking about this. I am going to forward this article to him. Pretty sure he’ll have a very good read. Many thanks for sharing!
I wanted to thank you for this great read!! I definitely enjoying every little bit of it I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you post…cool desktop
I need to to thank you for this excellent read!! I definitely enjoyed every little bit of it. I have you bookmarked to check out new things you post…
This cleared things up.
Your style is so unique compared to other folks I have read stuff from. I appreciate you for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I’ll just bookmark this site.
Super useful, thanks!
There’s definately a great deal to know about this topic. I really like all of the points you made.
Spot on with this write-up, I honestly believe that this website needs a great deal more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read more, thanks for the information!
So helpful, bookmarked!
MetaMask Chrome is a fantastic tool for crypto lovers. It enables easy access to DeFi projects and NFT marketplaces.
After looking into a handful of the blog posts on your web site, I really appreciate your technique of writing a blog. I book-marked it to my bookmark site list and will be checking back soon. Please visit my web site too and let me know how you feel.
This blog was… how do I say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something which helped me. Thanks a lot.
Kasyno online Wawada to licencjonowane kasyno przez Internet, które oferuje korzystne warunki dla graczy niezależnie od ich doświadczenia. Na odwiedzających ten portal zawsze czekają bonusy, oryginalne gry, ciekawe promocje. Wypłata wygranych działa, możesz otrzymać dodatkowy kod promocyjny, żeby debrać no-deposit. Kontynuuj rejestrację i baw się dobrze, zgarniając wielkie wygrane!
Thanks for sharing!
I’d have got to consult with you here. Which isn’t some thing Which i do! I love reading an article that will get people to feel. Also, appreciate your allowing me to comment!
MetaMask Extension is the best for DeFi enthusiasts. I use it daily for staking, swapping, and interacting with dApps securely.
I love it whenever people get together and share opinions. Great site, keep it up.
Aw, this was a really good post. Taking the time and actual effort to generate a good article… but what can I say… I procrastinate a whole lot and don’t seem to get anything done.
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular article! It’s the little changes that will make the most important changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
To grasp how stress can disrupt your time administration system and your productiveness, keep studying.
You produced some decent points there. I looked on the web for that problem and discovered most people will go in addition to using your internet site.
I’m pretty pleased to uncover this site. I need to to thank you for ones time due to this wonderful read!! I definitely liked every little bit of it and i also have you book-marked to see new things on your web site.
The remainder of the deck is placed in the middle of the table, face down.
Spot on with this write-up, I really feel this website needs a lot more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read more, thanks for the info.
There has been considerable research and analysis into the methods by which banks assess and monitor business loans, manage business financing risks, and price their products – and how these methods might be further developed and improved.
The Sith appear as main antagonists all through this story’s plot.
You do not must be an archery fan to name this Pixar film!
I could not refrain from commenting. Exceptionally well written!
Being a member of an funding membership in Dallas can open up numerous profitable opportunities to your funding portfolio.
Jamie now lives in Surrey with spouse Jodie and his three children.
That is the very best French meritorious army award, and was established within the 19th century by Napoléon Bonaparte.
So, the time has come to opt for the best fashion jewelry stores and get the right gift for your man.
Parts that might usually be chromed were lined in “black chrome,” such as the exhaust pipes and handlebars, or “gold chrome,” as have been the air-cleaner cowl and rear grab rail.
That is a good tip especially to those new to the blogosphere. Brief but very precise info… Appreciate your sharing this one. A must read article!
You made various nice points there. I did a search on the theme and found nearly all people will go along with with your blog.
Your style is very unique compared to other people I have read stuff from. Thank you for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I’ll just book mark this web site.
Howdy! I could have sworn I’ve visited this site before but after going through a few of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely happy I came across it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back frequently!
Greetings, I do believe your site could be having web browser compatibility problems. When I take a look at your site in Safari, it looks fine however, if opening in IE, it’s got some overlapping issues. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Besides that, fantastic website.
Hello! I simply want to give you a huge thumbs up for your excellent information you have right here on this post. I’ll be returning to your website for more soon.
This blog was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something that helped me. Kudos.
I absolutely love your blog.. Excellent colors & theme. Did you make this site yourself? Please reply back as I’m planning to create my own personal website and would like to learn where you got this from or just what the theme is named. Kudos!
Good day! I just wish to offer you a huge thumbs up for the great information you’ve got right here on this post. I’ll be coming back to your website for more soon.
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon every day. It’s always interesting to read articles from other authors and use a little something from other sites.
I was able to find good advice from your blog posts.
I needed to thank you for this very good read!! I definitely loved every bit of it. I have you saved as a favorite to look at new stuff you post…
Thanks for blogging and i enjoy the blog posting so no public comments.,,,,,,,,,,,
I have to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in writing this site. I really hope to see the same high-grade blog posts by you later on as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own, personal blog now 😉
Licencjonowane automaty do gry od Vavda, gry karciane mogą być dostępne dla wszystkich zainteresowanych bez depozytu. Jeżeli chcesz więcej, np. wypłacić wygrane, otrzymać bonus powitalny lub skorzystać z ciekawych kodów promocyjnych, musisz założyć konto na stronie. Rejestracja w kasynie Vavada jest maksymalnie uproszczona.
Your style is very unique compared to other people I’ve read stuff from. I appreciate you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I’ll just bookmark this page.
Nếu bạn thấy nội dung sai lệch hoặc không đáng tin, hãy rời khỏi trang ngay.
The next time I read a blog, Hopefully it won’t fail me just as much as this one. After all, I know it was my choice to read, but I actually believed you’d have something interesting to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of crying about something you could possibly fix if you were not too busy looking for attention.
Aw, this was an extremely nice post. Spending some time and actual effort to create a very good article… but what can I say… I procrastinate a whole lot and never manage to get nearly anything done.
Very good information. Lucky me I found your blog by chance (stumbleupon). I have saved as a favorite for later!
Cześć! Zapraszamy na oficjalną legalny stronę internetową Casino Vavada dla polskich graczy! Oferujemy bogaty wybór gier kasynowych od 44 uznanych twórców, takich jak Truelab, Pragmatic Play, IGT, Endorphina, Evolution Gaming, Playtech czy BGaming. Nasz program lojalnościowy obejmuje 5 poziomów członkostwa (od początkującego aż po platynowego), a w sekcji z grami na żywo możesz doświadczyć emocji dzięki profesjonalnym krupierom.
Hey your site looks a little bit weird in Opera on my office computer Mac .
I just love to read new topics from you blog.,*-’-
I must thank you for the efforts you’ve put in penning this blog. I really hope to view the same high-grade blog posts by you in the future as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my very own website now 😉
I couldn’t resist commenting. Very well written.
Although you might love a “healthy-looking” suntan, it is not your pores and skin’s pal.
Greetings! Very useful advice within this article! It’s the little changes that produce the largest changes. Thanks for sharing!
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a friend who was doing a little homework on this. And he actually bought me lunch due to the fact that I found it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending some time to talk about this issue here on your website.
There couple of interesting points over time here but I don’t determine if them all center to heart. You can find some validity but Let me take hold opinion until I investigate it further. Very good post , thanks and now we want a lot more! Put into FeedBurner also
I would like to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in penning this blog. I’m hoping to see the same high-grade content by you later on as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own website now 😉
I’m impressed, I must say. Really hardly ever do I encounter a weblog that’s each educative and entertaining, and let me let you know, you’ve hit the nail on the head. Your concept is outstanding; the problem is one thing that not enough individuals are talking intelligently about. I am very completely happy that I stumbled across this in my seek for something relating to this.
The 1967 Barracuda, while handsome enough, was still a disguised Valiant that really could not compete with its lustier Ford and GM rivals.
Good article. I definitely appreciate this website. Thanks!
The Taurus was a large vendor for Ford since its introduction in 1985, and when the company was on the lookout for a car to showcase a brand new engine it had designed with Yamaha, the Taurus acquired the nod.
You’ve made some decent points there. I checked on the web to learn more about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this website.
We’re over the works of thy fingers!
By developing a better understanding of psychological wellness and offering support, we are able to create a compassionate and inclusive society.
The upright that means invitations us to take risks for better progress in all points of life.
Elizabeth Cunningham, Nursing Auxiliary, Liverpool Health Authority.
The stock rebounded, you may choose to commerce.
The Werewolf Bot will DM you to let you know your function in addition to DM you lynching choices when it comes.
We’ve to keep opening extra markets.
Hello! I simply would wish to give you a huge thumbs up for any great information you have here within this post. I’ll be returning to your blog post for additional soon.
Saw the whole brief article. There is certainly some definitely helpful information and facts here. thank you. “There is no exercise better for the heart than reaching down and lifting people up.” by John Andrew Holmes..
I am always thought about this, thankyou for putting up.
Hi folks! Keen on the creativity—it’s brilliant. In fact, the presentation brings a cool touch to the overall vibe. Keep shining!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Your style is really unique in comparison to other people I have read stuff from. Thank you for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I’ll just bookmark this site.
I need to to thank you for this very good read!! I certainly enjoyed every bit of it. I have you saved as a favorite to check out new stuff you post…
It’s rare knowledgeable people during this topic, however, you seem like do you know what you’re discussing! Thanks
This would be the appropriate weblog for everyone who is wants to check out this topic. You know a lot its virtually hard to argue along (not that I really would want…HaHa). You actually put a fresh spin using a topic thats been discussed for years. Excellent stuff, just fantastic!
I am glad to be a visitant of this sodding site ! , regards for this rare info ! .
Good site you have got here.. It’s difficult to find good quality writing like yours nowadays. I seriously appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
Good post. I learn something new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon everyday. It will always be interesting to read content from other authors and practice something from other websites.
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular post! It is the little changes which will make the most significant changes. Many thanks for sharing!
Thanks for your whole work on this website. My mom take interest in doing research and it’s really easy to understand why. Most of us know all about the lively form you deliver rewarding strategies on your website and even improve response from other people about this point then our own simple princess is actually learning a great deal. Take pleasure in the remaining portion of the year. Your carrying out a really great job.
Thank you for having the time to discuss this topic. I truly appreciate it. I’ll stick a link of this entry in my site.
Have you considered about incorporating some social bookmarking buttons to these blogs. At least for twitter.
You are so awesome! I do not suppose I’ve truly read something like this before. So great to find somebody with some original thoughts on this subject. Seriously.. many thanks for starting this up. This web site is something that is required on the web, someone with some originality.
Wonderful post! We are linking to this particularly great content on our website. Keep up the great writing.
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this site. I really hope to view the same high-grade blog posts by you in the future as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own, personal website now 😉
I like it when folks get together and share opinions. Great website, stick with it!
After I originally left a comment I seem to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on whenever a comment is added I receive four emails with the same comment. Perhaps there is an easy method you are able to remove me from that service? Cheers.
To stop this from occurring, you need to place jack stands on the rear of the trailer before uncoupling it from the tow automobile.
I really prize your piece of work, Great post.
Hello. Very nice web site!! Man .. Beautiful .. Wonderful .. I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds also…I am glad to locate a lot of useful info here in the article. Thank you for sharing..
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your posts as long as I provide credit and sources back to your site? My blog is in the exact same area of interest as yours and my visitors would truly benefit from some of the information you provide here. Please let me know if this ok with you. Thanks!
This web page was last edited on 23 February 2024, at 17:08 (UTC).
certainly like your website but you have to check the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I find it very troublesome to tell the reality however I will certainly come again again.
Hi, It’s hard to find knowledgeable people on this topic, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
You produced some decent points there. I looked on the web for that problem and discovered most people is going together with with the internet site.
Turquoise is commonly used in numerous forms of jewellery, together with rings, pendants, earrings, and bracelets, as well as decorative objects such as beads and carvings.
The massive (wheelie bin) container encourages the “out of sight” rubbish mentality and invitations more rubbish to be disposed of.
After seeing the relative success of another waterway – Egypt’s Suez Canal, which opened in 1869 – America envisioned a shortcut through Central America as a way of strengthening its position as a two-ocean energy.
An outstanding share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a friend who has been doing a little homework on this. And he actually bought me dinner simply because I discovered it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending time to talk about this subject here on your website.
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful article. Many thanks for providing this info.
Manifest your allegiance to the arcane halls of Miskatonic University with this exquisite three-inch patch as your emblem of faculty pride.
All our merchandise are accredited by the government and bear lab-examined certificates of authenticity.
Glad to be one of the visitors on this awe inspiring internet site .
I am curious to find out what blog platform you’re using? I’m experiencing some small security problems with my latest website and I would like to find something more risk-free. Do you have any suggestions?
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to say that I’ve truly enjoyed browsing your blog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again soon!
Over an hour later all the forts have been destroyed or in shambles.
I believe so, but I can see I’ve an extended solution to go.
You have made some decent points there. I checked on the internet for more information about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this site.
Spot on with this write-up, I honestly believe this website needs a great deal more attention. I’ll probably be returning to see more, thanks for the advice!
Extra importantly, there’s substantial controversy about whether the CPI appropriately measures health care cost inflation – a problem which is especially pronounced in the CPI-E.
Hello there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this web site before but after looking at some of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m certainly delighted I found it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back often!
Also, individuals are discovering these applied sciences much more useful than human intervention.
You created some decent points there. I looked on the internet for the issue and found most individuals is going as well as along with your website.
Hi, you used to write excellent articles, but the last several posts have been kinda boring… I miss your super writing. Past several posts are just a little out of track!
You made some decent points there. I regarded on the internet for the difficulty and found most individuals will associate with with your website.
I’d like to thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this website. I really hope to see the same high-grade blog posts by you later on as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has encouraged me to get my very own site now 😉
The very next time I read a blog, Hopefully it does not disappoint me as much as this one. I mean, Yes, it was my choice to read through, but I really thought you’d have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you can fix if you weren’t too busy searching for attention.
Great article. I am dealing with a few of these issues as well..
May I just say what a comfort to uncover an individual who truly understands what they are talking about on the internet. You certainly realize how to bring a problem to light and make it important. A lot more people have to look at this and understand this side of the story. I was surprised that you are not more popular given that you most certainly possess the gift.
I was more than happy to discover this great site. I need to to thank you for ones time for this particularly fantastic read!! I definitely savored every part of it and I have you book marked to see new information on your site.
Good post! I have a random question for you. How do you get your blog indexed by bing? I have a related web blog.
so much superb information on here, : D.
This is tough. I’m not pointing fingers at you though, personally I think that its those that aren’t motivated to change.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
You clearly know your stuff. Wish I could think of something clever to write here. Thanks for sharing.
There is noticeably big money to comprehend this. I assume you’ve made specific nice points in features also.
Hi there, I found your blog via Google while searching for first aid for a heart attack and your post looks very interesting for me.
Somebody essentially assist to make severely posts I’d state. This is the very first time I frequented your web page and so far? I surprised with the research you made to create this particular post amazing. Excellent activity!
Is it not enjoyable if we constantly discuss subjects like this.
Wow, superb weblog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make running a blog look easy. The overall look of your web site is fantastic, let alone the content!
Howdy! I could have sworn I’ve visited your blog before but after browsing through some of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Regardless, I’m definitely happy I discovered it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back often.
I must thank you for the efforts you’ve put in penning this website. I really hope to view the same high-grade blog posts by you later on as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own, personal website now 😉
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem with your web site in internet explorer, would check this… IE still is the market leader and a big portion of people will miss your magnificent writing because of this problem.
It?s really a great and helpful piece of info. I?m satisfied that you simply shared this useful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
I’m truly enjoying the design and layout of your site. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a designer to create your theme? Exceptional work!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Gucci Outlet Online Great post This saved us a considerable time. Great site I am going to return back for addional info. Great site anyhow.
I was real pleased to find this site on bing, just what I was looking for : D likewise saved to my bookmarks .
Your style is unique in comparison to other people I’ve read stuff from. Thank you for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I will just bookmark this blog.
Sooner or later (which transit can last a long time) you are going to rid all by yourself of aged fears and restrictions, likewise as things that were programmed into you whenever you ended up pretty youthful!
hello there and thank you for your info – I’ve definitely picked up anything new from right here. I did however expertise a few technical issues using this web site, since I experienced to reload the site many times previous to I could get it to load correctly. I had been wondering if your web hosting is OK? Not that I’m complaining, but slow loading instances times will sometimes affect your placement in google and can damage your quality score if advertising and marketing with Adwords. Well I’m adding this RSS to my email and could look out for a lot more of your respective interesting content. Ensure that you update this again very soon..
I’m impressed, I must say. Really rarely do I encounter a blog that’s both educative and entertaining, and let me tell you, you’ve got hit the nail for the head. Your notion is outstanding; the pain is something that insufficient everyone is speaking intelligently about. We’re happy that we came across this at my look for some thing concerning this.
Hello, I do believe your web site could possibly be having web browser compatibility problems. Whenever I take a look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine however, if opening in I.E., it’s got some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to provide you with a quick heads up! Apart from that, excellent site!
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Thank you so much, However I am encountering troubles with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I can’t subscribe to it. Is there anybody else getting identical RSS problems? Anybody who knows the answer can you kindly respond? Thanks!
I was extremely pleased to find this web site. I need to to thank you for ones time due to this wonderful read!! I definitely really liked every part of it and i also have you bookmarked to check out new information on your blog.
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Thank you so much, However I am having issues with your RSS. I don’t understand why I am unable to subscribe to it. Is there anybody else having the same RSS issues? Anyone who knows the answer can you kindly respond? Thanx!!
*Nice post. I discover some thing much harder on various blogs everyday. Most commonly it is stimulating to study content from other writers and exercise a specific thing from their website. I’d opt to apply certain while using the content in this little blog whether or not you do not mind. Natually I’ll provide a link on your own internet weblog. Appreciate your sharing.
i like chaning tatum because he has a great body, just look at those chest muscles*
the blonde hair and eyes of Katherine Heigl is very attractive, she is very beautiful too.,
This site truly has all of the information I needed about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
of course we need to know our family history so that we can share it to our kids..
I have to express my appreciation for your generosity in support of women who really want help on in this concern. Your personal commitment to getting the message around appeared to be especially beneficial and have specifically made regular people like me to attain their endeavors. The interesting help signifies a lot to me and much more to my fellow workers. Thanks a ton; from each one of us.
I discovered your blog site on the search engines and check several of your early posts. Preserve within the really good operate. I recently extra your Feed to my MSN News Reader. Looking for toward reading much more of your stuff at a later time!…
MetaMask Extension is my go-to wallet. The security and accessibility it offers make it stand out from other crypto wallets.
Wow! This can be one particular of the most helpful blogs We’ve ever arrive across on this subject. Actually Excellent. I’m also a specialist in this topic therefore I can understand your effort.
Aw, it was a really good post. In concept I must put in writing similar to this additionally – spending time and actual effort to manufacture a excellent article… but exactly what do I say… I procrastinate alot and no means find a way to go carried out.
we have electrical fireplaces at home and we prefer it over conventional fireplaces’
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
Hello my friend! I wish to say that this post is awesome, great written and come with approximately all significant infos. I would like to peer more posts like this .
There are incredibly many details prefer that to take into consideration. This is a excellent denote mention. I provide thoughts above as general inspiration but clearly you can find questions much like the one you start up in which the most crucial factor might be in honest great faith. I don?t know if best practices have emerged around things like that, but I am certain that your chosen job is clearly labeled as a good game. Both boys and girls have the impact of just a moment’s pleasure, for the remainder of their lives.
This is some enjoyable stuff. It took me a while to locate this website but it was worth the time. I noticed this page was buried in google and not the number one spot. This web site has a ton of nice stuff and it does not deserve to be burried in the search engines like that. By the way Im going to save this website to my favorites.
Spot on with this write-up, I truly feel this site needs a lot more attention. I’ll probably be back again to read more, thanks for the info!
If so, you might be questioning the prices entailed with
this type of job.
Good day! I just want to give you a huge thumbs up for the excellent info you have here on this post. I will be coming back to your website for more soon.
Have a look at our guide showing regular supply and installation expenses.
Great article! We are linking to this great post on our website. Keep up the good writing.
They must also have the ability to use a one-to-three-year production warranty.
There are generally 2 pipelines which are each around 28mm in diameter consisting of the insulation.
I’d like to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in penning this site. I really hope to view the same high-grade blog posts from you in the future as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own, personal site now 😉
Having a broken thermostat may quit specific areas
of your home being cooled.
Excellent article. I’m facing many of these issues as well..
The most common and least expensive type of A/C is a mobile or
free standing air conditioning system.
This 0% barrel system will match the ₤ 5000 give that is readily available for air
source heatpump installations.
High-efficiency or specialized devices might have a greater upfront expense for setup.
Upgrading electric systems to suit the air conditioning system can contribute to the installment expense.
Costs are an overview just – a property study is needed for
a precise quote.
An excellent air conditioning system in the home offers a selection of advantages.
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
As soon as we prepare to go, this is what the setup procedure resembles.
We constantly value it if you can leave the installation website clear and produce an open path to it as well.
Talk with the specialists today and connect to our pleasant, educated team.
If you have another type of a/c brand you ‘d
like us to set up, just let us know.
What type of air conditioning system would certainly you like to install in your house?
Our water cooled down inner air conditioning systems are
installed inside.
It’s actually a nice and useful piece of info. I am happy that you just shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
Whats up, I’m ranking the crap out of “zygor guides”.
When I open up your RSS feed it gives me a bunch of garbled text, is the malfunction on my side?
You are so interesting! I don’t believe I have read through something like this before. So good to discover someone with a few genuine thoughts on this subject. Really.. thanks for starting this up. This website is one thing that is required on the web, someone with a little originality.
Everything is very open with a precise clarification of the issues. It was definitely informative. Your site is useful. Many thanks for sharing.
Excellent blog you have got here.. It’s hard to find excellent writing like yours these days. I seriously appreciate people like you! Take care!!
The following mail generally seems to get a number of page views. Make a decision advertise it? It’s offers a good creative ignore during elements. Reckon making a single thing precise or maybe a higher giving home elevators is a vital idea.
The output of each kind is gauged in British Thermal Devices, which are the
amount of warm gotten rid of in an hour.
Since “Independence Day” there has not been another great alien invasion flick… until now.
Comfortabl y, the article is really the freshest on this notable topic. I concur with your conclusions and also definitely will eagerly look forward to your incoming updates. Simply saying thanks will certainly not just be acceptable, for the extraordinary lucidity in your writing. I definitely will promptly grab your rss feed to stay privy of any kind of updates. De lightful work and also much success in your business dealings!
I like it whenever people get together and share views. Great website, stick with it.
Hi there! This post could not be written any better! Looking through this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He always kept talking about this. I will send this article to him. Pretty sure he’s going to have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
Hi, I do think this is an excellent site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I may come back yet again since I book marked it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.
Great article! We will be linking to this particularly great article on our site. Keep up the good writing.
An interesting discussion is definitely worth comment. There’s no doubt that that you ought to write more about this topic, it may not be a taboo subject but usually folks don’t talk about such topics. To the next! Many thanks.
The next time I read a blog, I hope that it does not disappoint me just as much as this one. After all, I know it was my choice to read through, however I actually thought you would probably have something interesting to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of moaning about something you could fix if you were not too busy looking for attention.
I blog frequently and I genuinely appreciate your information. Your article has truly peaked my interest. I am going to bookmark your blog and keep checking for new details about once per week. I subscribed to your Feed too.
Your style is so unique compared to other people I’ve read stuff from. Thank you for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I’ll just bookmark this web site.
Greetings! Very helpful advice within this article! It is the little changes that produce the greatest changes. Thanks for sharing!
I blog frequently and I genuinely appreciate your information. The article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to book mark your website and keep checking for new information about once a week. I opted in for your RSS feed too.
This website truly has all the information I wanted about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Spot on with this write-up, I honestly feel this web site needs a great deal more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read more, thanks for the info.
Right here is the right site for anyone who hopes to understand this topic. You realize a whole lot its almost tough to argue with you (not that I actually will need to…HaHa). You certainly put a fresh spin on a subject which has been written about for decades. Great stuff, just excellent.
Useful info. Fortunate me I discovered your website accidentally, and I am surprised why this coincidence didn’t happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Do you know this site is suggested by a number of other sites? Great work. Thank you very much!
There are incredibly plenty of details this way to take into consideration. Which is a wonderful examine mention. I supply the thoughts above as general inspiration but clearly you’ll find questions like the one you retrieve the spot that the most critical thing is going to be doing work in honest excellent faith. I don?t determine if recommendations have emerged about such things as that, but Most likely that the job is clearly recognized as a reasonable game. Both girls and boys feel the impact of simply a moment’s pleasure, through-out their lives.
Excellent post. I’m going through many of these issues as well..
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon every day. It will always be helpful to read through articles from other authors and practice a little something from their websites.
You’ve made some really good points there. I checked on the web for additional information about the issue and found most individuals will go along with your views on this site.
This is the perfect web site for everyone who wishes to understand this topic. You know a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I really will need to…HaHa). You certainly put a brand new spin on a topic that has been discussed for ages. Excellent stuff, just wonderful.
After study several of the blogs on the website now, and i genuinely much like your strategy for blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark site list and will also be checking back soon. Pls take a look at my website too and make me aware what you consider.
Immediately a bit of guests will continue across hotel rooms and obtain tied bus excursions, however, many with all the fancy car applications provide your own tour specialist. That just might help you browse through the neighborhood well you could an individual’s chose chauffeur. ??? ????
Black Ops Zombies is now available… […]Take a look here[…]…
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Hey, very informative blog post! Pleasee continue this awesome work.
Thank you for the sensible critique. Me and my neighbor were just preparing to do some research on this. We got a grab a book from our area library but I think I learned more clear from this post. I’m very glad to see such excellent information being shared freely out there.
The Star Trek score is great also, Kirk’s theme is cool, the title theme is beautiful, although I missed the fanfare.
The victims had been students on the east campus, however the murders happened nearer to the west campus.
Osborn suffered a lower from the constructing on his method out the window.
You can definitely see your skills in the work you write. The world hopes for even more passionate writers like you who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. Always go after your heart.
This is very interesting, You are a very skilled blogger. I have joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking more of your great post. Also, I have shared your site in my social networks!
i think that gun control is a must because more guns means more deaths-
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through a single thing like that before. So good to discover somebody with unique thoughts on this topic. Really.. many thanks for starting this up. This site is something that’s needed on the web, someone with a bit of originality.
This is really exciting, You’re an especially skilled writer. I’ve enrolled with your feed plus look ahead to enjoying the excellent write-ups. Additionally, I’ve shared your web sites inside our myspace.
I am only commenting to let you know of the remarkable experience our girl encountered reading the blog. She noticed many pieces, which included how it is like to possess an amazing giving nature to get certain people really easily learn certain multifaceted things. You undoubtedly exceeded visitors’ desires. I appreciate you for rendering the important, healthy, informative as well as easy tips about the topic to Kate.
fapturbo review Spot lets start work on this write-up, I must say i think this website wants additional consideration. I’ll probably be once again to see a great deal more, thank you that information.
I’m impressed, I must say. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both equally educative and entertaining, and let me tell you, you’ve hit the nail on the head. The problem is something too few men and women are speaking intelligently about. I’m very happy that I came across this during my search for something concerning this.
This website was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I have found something that helped me. Kudos!
Introducing to you the most prestigious online entertainment address today. Visit now to experience now!
It’s difficult to find experienced people in this particular topic, but you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Saved as a favorite, I really like your website!
You’ve made some decent points there. I looked on the net to find out more about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this web site.
Hi this is somewhat of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding skills so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated.
Can I just now say what relief to discover somebody who really knows what theyre speaking about on-line. You definitely have learned to bring a challenge to light and produce it critical. The diet need to check out this and can see this side on the story. I cant believe youre no more well-liked when you absolutely possess the gift.
I think this is one of the most significant information for me. And i’m glad reading your article. But should remark on some general things, The web site style is perfect, the articles is really great : D. Good job, cheers
I’m impressed, I must say. Seldom do I come across a blog that’s both equally educative and entertaining, and let me tell you, you have hit the nail on the head. The problem is an issue that too few folks are speaking intelligently about. Now i’m very happy that I came across this during my hunt for something relating to this.
Good article! We are linking to this particularly great content on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Spot on with this write-up, I really feel this site needs a great deal more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read more, thanks for the information!
Greetings! Very useful advice within this post! It is the little changes which will make the largest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
Great Share! Aw, this was a really nice post. In idea I would like to put in writing like this additionally – taking time and actual effort to make a very good article but what can I say I procrastinate alot and by no means seem to get something done.
Oh my goodness! an incredible article dude. Thank you Nonetheless I am experiencing subject with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anyone getting an identical rss downside? Anybody who knows kindly respond. Thnkx
i have a passion on anything that is automotive related. i love to attend car shows too::
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I have discovered It absolutely useful and it has aided me out loads. I’m hoping to give a contribution & assist other customers like its aided me. Great job.
I just could not leave your web site before suggesting that I actually enjoyed the standard info an individual provide on your visitors? Is gonna be back regularly in order to check up on new posts.
Can I just say what a relief to uncover someone that really understands what they’re discussing on the net. You definitely understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. A lot more people really need to read this and understand this side of the story. It’s surprising you aren’t more popular because you most certainly possess the gift.
When I originally commented I seem to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now whenever a comment is added I receive 4 emails with the exact same comment. Is there an easy method you can remove me from that service? Thanks a lot.
Aw, that was a really good quality post. In theory I’d like to write like this too – taking time and real effort to make a good article… but what can I say… I procrastinate alot and also never seem to get something done.
google and other search engines would always love organic seo and natural link building;;
There may be clearly a bunch to understand this particular. I believe you’ve made certain pleasant points within features also.
Good article. I certainly appreciate this website. Keep it up!
The when I just read a weblog, I really hope who’s doesnt disappoint me about that one. After all, I know it was my option to read, but I personally thought youd have some thing interesting to state. All I hear is often a lot of whining about something you could fix if you ever werent too busy looking for attention.
Aw, this was a very nice post. In idea I wish to put in writing like this additionally ?taking time and precise effort to make a very good article?but what can I say?I procrastinate alot and certainly not seem to get something done.
Wow! This could be one particular of the most beneficial blogs We have ever arrive across on this subject. Actually Fantastic. I’m also an expert in this topic therefore I can understand your effort.
I used to be able to find good info from your content.
This is a topic that’s near to my heart… Take care! Where are your contact details though?
This is a topic that’s near to my heart… Take care! Where are your contact details though?
Howdy, I do believe your blog could be having browser compatibility issues. When I take a look at your website in Safari, it looks fine however, if opening in I.E., it’s got some overlapping issues. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Apart from that, excellent blog.
i use Garmin GPS whenever i go out, Garmin GPS is very reliable.
Sometimes, blogging is a bit tiresome specially if you need to update more topics.,-`”.
I think this is one of the most significant information for me. And i’m glad reading your article. But should remark on some general things, The web site style is perfect, the articles is really great : D. Good job, cheers
if you really need to become expert in driving, your really need to enroll in a driving school,.
You seem to have a lot of confidense in the things you do. Nice post also! .
Very good written article. It will be helpful to anybody who usess it, including myself. Keep up the good work – can’r wait to read more posts.
countries that do need lots of financial aids are those coming from Africa. i could only wish that their lives would become better**
I savour, result in I found just what I was taking a look for. You’ve ended my four day lengthy hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
very nice put up, i actually love this web site, keep on it
To keep prices low, begin with term life insurance and invest your savings elsewhere.
Saved as a favorite, I like your blog.
Can I simply just say what a relief to discover somebody who truly knows what they are talking about over the internet. You certainly realize how to bring a problem to light and make it important. More and more people should read this and understand this side of the story. I was surprised you are not more popular because you surely have the gift.
Weddings in Abu Dhabi are luxurious events, where individuals praise the recent start of their life.
Aw, this was a really good post. Finding the time and actual effort to create a very good article… but what can I say… I hesitate a whole lot and never manage to get anything done.
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular article! It is the little changes that produce the largest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
Getting individual lashes utilized is generally inexpensive, but these who’re adept with tiny strands and minute drops or items of adhesive may have no downside filling in their own lash traces.
Excellent commentary on that subject. We appreciate your knowledge that you to leave with us!
Only a quickly hello and also to appreciate talking about your ideas with this page.
It is perfect time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I have read this post and if I could I desire to suggest you some interesting things or tips. Perhaps you can write next articles referring to this article. I wish to read more things about it! Miss Global warming
The next year, it was re-branded as Halloween Horror Nights, advertised as the “second annual event”.
I am extremely impressed with your writing skills as well as with the layout on your blog. Is this a paid theme or did you modify it yourself? Anyway keep up the excellent quality writing, it is rare to see a nice blog like this one nowadays..
This really is a very amazing powerful resource that you’re offering and you just provide it away cost-free!! I really like discovering websites ones understand the particular valuation on giving you fantastic learning resource for zero cost. We truly dearly loved examining these pages. Be thankful!
you have a fantastic blog here! do you wish to earn some invite posts on my blog?
That is a very good tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere. Brief but very precise info… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read article!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
I was suggested this website by my cousin. I’m not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my problem. You are wonderful! Thanks!
Very good article! We are linking to this particularly great post on our website. Keep up the good writing.
home furnitures that uses hardwoord is a great option because hardwoods last longer*
So, naturally, with these two together, movie magic is accomplished.
I really like reading through a post that can make men and women think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment.
Hello there, have you by chance thought about to publish regarding Nintendo or PS handheld?
I really delighted to find this website on bing, just what I was searching for : D also saved to fav.
Will not simply turn a very important thing such as duty money back guarantee towards a bad thing enjoy i . d break-ins.
I blog quite often and I seriously appreciate your information. Your article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to bookmark your website and keep checking for new information about once a week. I subscribed to your Feed as well.
This web site really has all the info I needed about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
The very next time I read a blog, I hope that it does not fail me as much as this particular one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read through, nonetheless I really believed you would probably have something helpful to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something you could fix if you were not too busy looking for attention.
I like this web blog so much, saved to my bookmarks .
I love reading a post that can make people think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment.
There are quite a lot of eating places and meals factors in Germany.
Sergio Pininfarina had personally dealt with his carrozzeria鈥檚 Ferrari account since his father had landed it in 1952.
Can I simply say what a relief to find someone that genuinely understands what they’re talking about over the internet. You definitely realize how to bring a problem to light and make it important. A lot more people need to read this and understand this side of the story. I was surprised that you aren’t more popular given that you definitely have the gift.
Feel honoured to stand on the Mera , and get pleasure from probably the most splendi vista of summits encompassing Mt.
Would you may have more free intervals than classes, would you be making extra time for Quidditch apply than the choir, or would you be utilizing a time-turner to make up for missed courses?
Your blog is amazing dude. i love to visit it everyday. very nice layout and content “
This is a appropriate blog for everyone who is wishes to find out about this topic. You understand a great deal its practically challenging to argue with you (not that I just would want…HaHa). You certainly put a brand new spin on a topic thats been discussed for years. Great stuff, just fantastic!
HOMER: i want the monogram to say m..a..x..p..o..w.(homer gets inturupted)SALE LADY: sir normally its just the initials that go on the monogramHOMER: Max Powers does not abriviate each letter is just as important as the last. or more important. no no as important
Hello there, I do believe your site could possibly be having web browser compatibility problems. Whenever I look at your website in Safari, it looks fine however, if opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other than that, great blog!
Everything is very open with a precise description of the issues. It was definitely informative. Your website is useful. Thanks for sharing.
Hi there! This article couldn’t be written much better! Looking through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He continually kept talking about this. I am going to send this information to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
I have been exploring for a little bit for any high-quality articles or blog posts on this kind of area . Exploring in Yahoo I finally stumbled upon this web site. Reading this information So i am glad to express that I have a very good uncanny feeling I came upon exactly what I needed. I most no doubt will make sure to do not omit this web site and provides it a glance a relentless basis.
plastic bathroom faucets woud eaily break compared to bronze bathroom faucets-
You can definitely see your expertise in the paintings you write. The world hopes for even more passionate writers such as you who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. Always go after your heart
You should be a part of a contest for one of the finest blogs on the internet. I’m going to recommend this blog!
This site is often a walk-through for all of the data it suited you with this and didn’t know who need to. Glimpse here, and you’ll definitely discover it.
Having read this I thought it was rather enlightening. I appreciate you taking the time and energy to put this article together. I once again find myself personally spending way too much time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it.
Good day! I just want to give you a big thumbs up for your excellent information you have got here on this post. I will be coming back to your web site for more soon.
There’s definately a great deal to find out about this topic. I love all of the points you’ve made.
You should take part in a contest for one of the most useful websites online. I am going to recommend this blog!
Hi, I do believe this is a great site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I will return once again since i have saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide others.
Everything is very open with a really clear clarification of the challenges. It was definitely informative. Your site is very helpful. Many thanks for sharing.
I blog frequently and I genuinely thank you for your information. The article has really peaked my interest. I will bookmark your site and keep checking for new details about once a week. I opted in for your Feed as well.
You are so awesome! I don’t think I’ve read through anything like that before. So nice to find another person with some genuine thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This web site is one thing that is needed on the internet, someone with some originality.
Hey there! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could locate a captcha plugin for my comment form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having trouble finding one? Thanks a lot!
Hi, I do think this is a great website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m going to revisit once again since I saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide other people.
As a teacher, I grade a lot of writing assignments. That’s a hard habit to break so I give you a strong A+ for this article. It’s interesting and well-written.
Thousands and thousands of birds and marine animals perish each year from either ingesting or getting caught up in the billions of plastic bags that Americans use each year.
I really love your site.. Pleasant colors & theme. Did you create this site yourself? Please reply back as I’m trying to create my own personal website and would like to find out where you got this from or exactly what the theme is named. Appreciate it!
The substitutes often are withdrawn from production.
You should take part in a contest for one of the best sites on the net. I am going to highly recommend this web site!
In 1988, a committee was arrange underneath EEC President Jacques Delors to begin changing the EMS to provide favorable starting conditions for the transition to Economic and Monetary Union (EMU).
Nonetheless, a group doesn’t have to have official nonprofit status in an effort to get a site.
Many firstcomers face the problem of arranging funds without first showing some traction that suggests potential success.
Everything is very open with a clear clarification of the issues. It was truly informative. Your website is useful. Many thanks for sharing.
The highest-stage of turquoise that is of course laborious enough for use is known as ‘pure’ or ‘untreated’ turquoise.
Construct your brand consciousness with probably the most compact formatting of visible signage without addressing by way of monotonous descriptions.
You’ve made some decent points there. I checked on the internet for more info about the issue and found most people will go along with your views on this website.
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular article! It is the little changes which will make the most important changes. Thanks for sharing!
You need to take part in a contest for one of the greatest blogs on the net. I am going to recommend this site!
This is a topic which is close to my heart… Take care! Exactly where can I find the contact details for questions?
I really love your website.. Pleasant colors & theme. Did you build this web site yourself? Please reply back as I’m hoping to create my own personal blog and would love to know where you got this from or just what the theme is called. Appreciate it.
Great blog you have here.. It’s difficult to find quality writing like yours these days. I seriously appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
When the short interest has reached a maximum, the company announces it has made a deal with its creditors to settle its loans in exchange for shares of stock (or some similar kind of arrangement that leverages the stock price to benefit the company), knowing that those who have short positions will be squeezed as the price of the stock sky-rockets.
Oh my goodness! Impressive article dude! Many thanks, However I am experiencing difficulties with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I cannot subscribe to it. Is there anyone else getting identical RSS problems? Anyone that knows the solution will you kindly respond? Thanks!!
This is going to make it more difficult for finances to meet up to the liabilities of the income until and unless they become more risky.
You are so awesome! I do not suppose I have read anything like that before. So great to find somebody with some unique thoughts on this issue. Really.. thanks for starting this up. This web site is one thing that is needed on the internet, someone with some originality.
The troubled economy has had losses pouring in from different sections, so the banks claw on to any revenue source they can lay their hands on.
Greetings! Very useful advice within this article! It’s the little changes that produce the most important changes. Thanks for sharing!
Everyone loves it when individuals get together and share thoughts. Great site, continue the good work.
Excellent article. I certainly appreciate this site. Keep writing!
Everyone’s overlooked this foremost concept. I’d wish to be capable of getting my eyes on the assets which you utilized to expose this. Make sure you stick to your writing.
I like it when folks get together and share thoughts. Great blog, keep it up.
It’s nearly impossible to find knowledgeable individuals within this topic, and you be understood as guess what happens you’re speaking about! Thanks
After exploring a number of the blog articles on your website, I really appreciate your way of writing a blog. I saved it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back soon. Take a look at my web site as well and tell me how you feel.
Automotive enthusiasts go gaga over braided stainless steel brake lines — the steel-encased Teflon flexes significantly less than odd rubber hoses, making for a firmer pedal feel.
His fourth look for the membership in opposition to Toulouse on 15 May 2017 noticed him play a vital position together with his impressive saves, including saving a penalty, in a 1-1 draw.
So, provide chain administration might be defined as “the methodical, key coordination of customary business capacities and strategies over all enterprise capacities inside a selected group and crosswise over organizations inside the manufacturing community, for the reasons for enhancing the long haul execution of the individual organizations and the stock community typically”.
Dual-pace pumps supply some power financial savings, but they lack the pliability of variable-speed pumps.
Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular post! It is the little changes which will make the most significant changes. Many thanks for sharing!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Hello there! I just would like to offer you a huge thumbs up for the great information you have right here on this post. I’ll be returning to your web site for more soon.
Pretty! This was an incredibly wonderful post. Thank you for providing this information.
This is the perfect website for anyone who really wants to understand this topic. You know a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I really would want to…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a subject that’s been discussed for decades. Wonderful stuff, just wonderful.
I love it when people get together and share thoughts. Great website, stick with it!
A fascinating discussion is definitely worth comment. There’s no doubt that that you need to write more about this subject, it may not be a taboo matter but generally people don’t discuss such issues. To the next! Best wishes!
I was able to find good information from your blog posts.
This is a topic that is close to my heart… Take care! Exactly where are your contact details though?
Awesome insights!
Excellent write-up. I certainly love this site. Thanks!
sex nhật hiếp dâm trẻ em ấu dâm buôn bán vũ khí ma túy bán súng sextoy chơi đĩ sex bạo lực sex học đường tội phạm tình dục chơi les đĩ đực người mẫu bán dâm
Hello, I do think your web site could possibly be having web browser compatibility problems. When I take a look at your web site in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it’s got some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to give you a quick heads up! Aside from that, wonderful website.
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Thank you so much, However I am having problems with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I am unable to subscribe to it. Is there anybody else getting identical RSS issues? Anyone that knows the answer will you kindly respond? Thanks.
I really enjoyed reading this! Your writing style is engaging, and the content is valuable. Excited to see more from you!
The very next time I read a blog, I hope that it does not fail me as much as this particular one. After all, Yes, it was my choice to read through, nonetheless I truly thought you would have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something you can fix if you were not too busy looking for attention.
After exploring a few of the blog posts on your blog, I seriously like your technique of blogging. I book-marked it to my bookmark site list and will be checking back soon. Please visit my web site as well and let me know your opinion.
Hi, I do believe this is a great web site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to revisit yet again since i have saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide others.
Everything is very open with a really clear clarification of the issues. It was definitely informative. Your website is extremely helpful. Many thanks for sharing.
This post is very helpful! I appreciate the effort you put into making it clear and easy to understand. Thanks for sharing!
Right here is the right web site for everyone who wishes to understand this topic. You know so much its almost tough to argue with you (not that I really will need to…HaHa). You definitely put a brand new spin on a subject that’s been discussed for years. Excellent stuff, just great.
I love reading a post that will make men and women think. Also, many thanks for allowing for me to comment.
Howdy! I could have sworn I’ve visited your blog before but after looking at many of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely happy I discovered it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back often!
I was very pleased to discover this great site. I want to to thank you for ones time for this fantastic read!! I definitely liked every bit of it and i also have you book-marked to check out new information on your web site.
Great article. I will be experiencing a few of these issues as well..
I must thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this site. I’m hoping to see the same high-grade blog posts from you later on as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own, personal blog now 😉
We are often instructed by purchasers that they haven’t got a set funds for an occasion.
I’d like to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in writing this site. I am hoping to check out the same high-grade content by you later on as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my very own blog now 😉
The Week in Chess stories that Kramnik and Topalov should not taking part because the event had insufficient prize money.
Rotate collections to keep your room at the top of its form.
AFC Telford United supremo Lee Carter has dropped a bombshell by warning there might not be a club in 12 months’ time.
It is the procedure of distributing the wealth of an investor among various asset classes for investment.
Can I simply just say what a relief to uncover somebody that genuinely knows what they’re talking about over the internet. You actually realize how to bring an issue to light and make it important. A lot more people must read this and understand this side of the story. I can’t believe you are not more popular since you surely have the gift.
In an interview with Bloomberg, OKX President Hong Fang said OKX will continue building banking relationships in Hong Kong and different jurisdictions.
The main company focuses on designing, growth and implementation.
However, as most of the writers for the Eighth Physician Adventures had also written for the Virgin series, many elements from the brand new Adventures began to appear in each the EDAs and the Past Doctor Adventures (which replaced the Lacking Adventures), and such continuity has been broadly maintained.
Moreover microwave, kettle and toaster kitchen appliances are available.
However, in many jurisdictions the members of the company are permitted to ratify transactions which would otherwise fall foul of this principle.
In England, astrology reached its high level during the reign (1558-1603) of Queen Elizabeth I. However with the discoveries and theories of astronomers Copernicus and Galileo in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, respectively, astrology and astronomy diverged, by no means to be reunited below the same scientific banner.
At the end of the 13th century, window artists additionally applied extra layers of coloured glass to their windows, then engraved the higher layers to reveal the colours beneath.
That is a really good tip especially to those fresh to the blogosphere. Simple but very precise information… Thank you for sharing this one. A must read post.
Well-liked iris cultivars embody Japanese, spuria, aril, bearded and yellow flag.
MIAMI, FL – An experienced broker in the precious metals market, Bill Hionas is now leading Pan American Metals of Miami (PAMM), a precious metals brokerage based in Miami, Florida.
Stock Market- it’s the place wherever numerous individuals trade globally and earn the utmost come back on investment.
Rev.J.T. Hill of Provo; 4 sisters, Miss Willie Hill, Provo, Mrs.
Otherwise, you may have to dish out money for the travel and resort.
The rate of interest posed on this type of bond is stated rate of interest.
It’s a special Rakhi for bhabhi to strengthen the bond with the sister-in-legislation.
Due to its tendency to compound different risks, it is tough or inconceivable to isolate liquidity threat.
Beforehand, crew cabs were provided solely in 3/4-ton-and-up pickups.
A line colloquially identified because the Berlin draw is often utilized by high-stage players to agree to an early draw: 1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bb5 Nf6 4.0-0 Nxe4 5.d4 Nd6 6.dxe5 Nxb5 7.a4 Nbd4 8.Nxd4 Nxd4 9.Qxd4 d5 10.exd6 e.p.
Good blog you have here.. It’s difficult to find good quality writing like yours nowadays. I truly appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
Take the steps instead of elevators or escalators whenever attainable.
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you writing this write-up plus the rest of the website is extremely good.
Good info. Lucky me I ran across your site by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve book marked it for later!
Right here is the right web site for everyone who wants to find out about this topic. You know so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want to…HaHa). You definitely put a fresh spin on a topic that’s been written about for years. Great stuff, just wonderful.
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you writing this write-up and the rest of the website is also very good.
Having read this I thought it was very informative. I appreciate you finding the time and effort to put this information together. I once again find myself personally spending a significant amount of time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worthwhile!
You can infact bifurcate metals into several categories like precious metals, non precious metals, scrap metals, alloys, base metals etc.
Spot on with this write-up, I honestly believe that this amazing site needs far more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read more, thanks for the information.
One other version of the Outdated and New Town names says that the railroad depot was moved by half a mile to forestall hill begins, and business owners quickly followed it, displacing the commerce of the city to Entrance Road of ‘New City’ whereas the homes had been nonetheless in ‘Old Town’ with the spring; when the hearth burned down ‘Outdated Town’, ‘New City’ remained.
Very good post. I am going through some of these issues as well..
Home-based business owners can deduct things like a home office, telephone, internet service and office supplies.
The doctors and hospitals are private entities, which distinguishes the Canadian system from the British socialized medicine system, in which doctors are employees of the government.
The CEF was geared up with Allied weapons such as the .Forty five (11.Forty three mm) Thompson submachine gun and .50 (12.7 mm) Browning machine gun.
In a 2015 study, threat communication to people who had members of the family with dementia passed off, and a mannequin was developed that closely options shared resolution-making processes.
I absolutely love your site.. Excellent colors & theme. Did you build this web site yourself? Please reply back as I’m hoping to create my own website and would love to learn where you got this from or just what the theme is named. Cheers!
As virtually people know that traditional and antique gold-jewellery has all the time been widespread in India.
Conrad Strauss reportedly conversed with investors on China breaking out of a continuing losing streak.
Electrical Requirements: The pump room ought to be designed to meet local electrical codes and provide easy access to electrical panels.
Criticism mounted in ensuing a long time, and victims demanded redress for his or her losses.
Having read this I thought it was extremely informative. I appreciate you taking the time and energy to put this information together. I once again find myself spending way too much time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve visited your blog before but after browsing through some of the posts I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m certainly pleased I discovered it and I’ll be bookmarking it and checking back often!
If you don’t want to draw a bar graph, you can glue the pennies directly onto poster board to create a graph.
It ought to be famous that this isn’t true in a large number of other cultures / languages.
Margin trading requires risk management.
Richmont Graduate College is a Christian graduate college located in Chattanooga with a CACREP accredited clinical mental health counseling program in addition to other ministry related degrees and a student population near 300.
Trusts are, in easy phrases, organizations which are formed to assist the individuals of society on different grounds and levels.
In Could 1864, Union General Jefferson C. Davis, below the command of Major General William Tecumseh Sherman, attacked and captured Rome when the outflanked Confederate defenders retreated below command of Main General Samuel Gibbs French.
We hope to recreate locations like Camp David, the Kremlin (and the tunnels beneath it), the bone-strewn catacombs beneath Paris, Hong Kong’s junk-filled harbor, the London underground and more.
However, immediately auditors pay shut consideration to administrator activities in these environments.
I blog quite often and I truly thank you for your content. Your article has truly peaked my interest. I’m going to bookmark your blog and keep checking for new details about once a week. I opted in for your RSS feed too.
Greetings, I think your website may be having web browser compatibility issues. Whenever I take a look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine however, when opening in Internet Explorer, it’s got some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to provide you with a quick heads up! Apart from that, great website!
I must thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this site. I’m hoping to check out the same high-grade blog posts from you later on as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my very own blog now 😉
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon on a daily basis. It’s always exciting to read through articles from other authors and practice something from their web sites.
Hafer, T.J. (31 October 2012).
This web site definitely has all the info I wanted about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
They are ranked thirteenth finest Journey Administration Company by Journey Weekly with $1.23 billion in gross sales in 2021.
Should you have been a pupil in 1999, you possible copied notes that have been proven on what device?
Adding yogurt and/or cottage cheese contributes to bone growth and digestive system well being of your French bulldog and most French bulldogs love the style.
Very good article. I’m experiencing some of these issues as well..
Begin with very wet hair when styling.
While it was first created in the late 1940s, the iconic plastic gingerbread men pawns weren’t introduced until 1967.
I like reading through an article that will make people think. Also, thanks for permitting me to comment.
After looking at a number of the articles on your website, I seriously appreciate your way of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark site list and will be checking back soon. Please visit my website too and let me know how you feel.
Indian investors are deciding to trust professional stock market analytics and experts to help them multiply their money.
Oh my goodness! Impressive article dude! Many thanks, However I am going through difficulties with your RSS. I don’t know why I am unable to join it. Is there anyone else having similar RSS issues? Anyone that knows the solution will you kindly respond? Thanks!
While researchers such as George Haley, Vladimir Kvint, Hernando de Soto, Usha Haley, and several professors from Harvard Business School and Yale School of Management have described activity in countries such as India and China, how a market emerges is little understood.
I couldn’t resist commenting. Perfectly written.
Beginning in the north-west it can serve the next stops.
Pezdek’s reasoning. Particularly, they agreed that regression to the imply was current in their own information and contributed to the overall changes in confidence on the second check.
Additionally try the tonequest net site for far more.
Bertram Cope, Assistant Accountant General, Ministry of Pensions & Nationwide Insurance.
Or choose the Console button within the Navigation Bar to create a person account.
Dolls: Antique and even simply retro dolls are often hollow and subsequently simple to slide wiring into.
Hitzacker is situated on the confluence of the River Jeetzel with the Elbe.
While anxiety attacks could be distressing, they’re usually not life-threatening.
As with all other types of legal offers, the other party may accept the offer, reject it (in which case the offer is terminated), make a counteroffer (in which case the original offer is terminated), or not respond to the offer (in which case the offer terminates by the expiration date in it).
Usually, implicit curves fail the vertical line take a look at (meaning that some values of x are associated with a couple of worth of y) and so usually are not essentially graphs of functions.
It wasn’t until on 29 November 2017 when he made his first look of the season, beginning the whole game, in a 2-zero in opposition to Troyes.
At the age of nine the household moved to cut Bank, Montana , where her father labored for the good Northern Railroad.
Our our bodies are flooded with adrenaline, dopamine, oxytocin, endorphins and more.
Decision Support Systems. Economics and Information Systems.
Duquesne head coach Elmer Layden is credited with devising the system of hand indicators that officials use today.
Spot on with this write-up, I absolutely believe that this amazing site needs much more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read through more, thanks for the advice.
Which leads properly into the next factor that went proper.
Brake pads and calipers are another way to upgrade your braking system — and there are plenty of options available.
Accessed Sept. Medline Plus.
The board and piece colors are funky, to say the least, however the set is highly usable; in reality you may arrange a place, shut the case, and expect to search out the place still there whenever you return to it.
Relying in your purchasing and eating habits, a single meal out for 2 would possibly ring up at about the identical value as a week’s worth of groceries for those same two folks.
For that reason, we must opt for the firm, which has done well in the stock market arena; it is also crucial to look for nothing but the very best in this niche market segment.
Some law schools give all applicants a prompt for the essay.
International exchange calculator is easily obtainable and even individuals with little knowledge can use it and may earn a huge sum of money.
Hello there! This post could not be written any better! Looking through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He continually kept preaching about this. I’ll send this post to him. Pretty sure he’ll have a great read. Thanks for sharing!
As you probably recall, all it’s worthwhile to do is cut your paper into a square and then fold it into layers of smaller squares.
Martucci, Joe (June 3, 2020).
Hi, I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m going to return yet again since I bookmarked it. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to help others.
This dialogue will try to point out the origins of the roots of such religious legends and folklore from a lot older civilisations, in order to dissociate it from historicity.
You’re so awesome! I don’t think I’ve truly read a single thing like this before. So nice to find someone with genuine thoughts on this issue. Really.. thanks for starting this up. This site is something that’s needed on the web, someone with some originality.
In Darth Maul: Shadow Hunter, by Michael Reaves, Darth Sidious sends his apprentice, Darth Maul, to analyze the traitor who leaked the key of his plan to take down the Republic.
TopBuild Corp. Good Fortune: The Irani Firoza is considered a logo of wealth and prosperity and is believed to attract good luck and success to its wearer.
Very good information. Lucky me I came across your blog by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve bookmarked it for later.
I enjoy reading through an article that can make men and women think. Also, many thanks for allowing for me to comment.
If you have this document then you will be in a much better position to protect yourself against any potential litigation that may arise form working with a private investor source.
After looking at a handful of the blog posts on your web site, I really appreciate your way of writing a blog. I bookmarked it to my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back soon. Please visit my web site too and tell me what you think.
Some of our new workforce members proved to be “maximalists” – desirous to do everything, special-case numerous stuff, and stick as close to actuality as attainable.
A growing number of auto insurers encourage car owners to have the vehicle identification number (VIN) etched into the window, the engine and other parts of their vehicle to discourage thieves from stealing the car.
The 2008 presidential campaign of Bob Barr, former Congressman of Georgia started on Might 12, 2008.
1. Discover a room where you possibly can put the dog’s meals bowl and keep the door closed such because the bathroom or a back storeroom while they’re feeding.
McCormick, Annie; Ileto, Christine (September 15, 2020).
This page definitely has all of the info I wanted about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Oh my goodness! Awesome article dude! Thanks, However I am encountering difficulties with your RSS. I don’t understand why I can’t subscribe to it. Is there anybody else getting similar RSS problems? Anybody who knows the answer will you kindly respond? Thanx!
bookmarked!!, I like your site.
Next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesn’t fail me just as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, but I genuinely believed you’d have something helpful to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of complaining about something you could fix if you weren’t too busy seeking attention.
I could not refrain from commenting. Perfectly written.
In the long-term, using a credit card properly and paying off the balance can help establish a credit history and bump up your credit score, which will come in handy when you need an important loan, for a house or car, for example.
It’s nearly impossible to find educated people in this particular subject, however, you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Everything is very open with a precise explanation of the issues. It was really informative. Your website is very helpful. Many thanks for sharing.
I like reading through a post that can make men and women think. Also, thanks for allowing me to comment.
Excellent article. I definitely appreciate this website. Stick with it!
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Rarely do I encounter a blog that’s equally educative and engaging, and without a doubt, you have hit the nail on the head. The problem is something which too few people are speaking intelligently about. Now i’m very happy I found this in my search for something regarding this.
Compact fluorescent bulbs even have come on the scene as “inexperienced” alternatives that cost just a little more but last significantly longer than their incandescent counterparts.
This site was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something that helped me. Kudos.
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a co-worker who had been doing a little research on this. And he in fact ordered me dinner simply because I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending time to talk about this topic here on your blog.
bookmarked!!, I really like your site!
Right here is the right site for anybody who hopes to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost tough to argue with you (not that I personally will need to…HaHa). You certainly put a fresh spin on a subject that has been written about for many years. Wonderful stuff, just great.
You’re so cool! I don’t believe I’ve truly read through anything like that before. So great to discover another person with a few unique thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This web site is something that’s needed on the web, someone with a bit of originality.
Pretty! This was a really wonderful article. Thank you for providing these details.
While the motives behind the space race could not have been purely based upon a want to increase our scientific information, that on no account diminishes the accomplishments made by both international locations.
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon every day. It’s always exciting to read articles from other writers and practice a little something from their websites.
With the win, Carlsen took a 3½-2½ lead in the best-of-14-game match.
Can I just say what a comfort to uncover someone that really understands what they’re talking about on the net. You actually understand how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people really need to read this and understand this side of the story. It’s surprising you’re not more popular given that you certainly possess the gift.
Aw, this was an extremely nice post. Taking the time and actual effort to produce a very good article… but what can I say… I hesitate a whole lot and don’t seem to get nearly anything done.
I’m amazed, I must say. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both equally educative and amusing, and let me tell you, you have hit the nail on the head. The issue is something which not enough men and women are speaking intelligently about. I am very happy that I found this in my search for something regarding this.
Hello! I just wish to offer you a huge thumbs up for your excellent information you’ve got right here on this post. I am returning to your web site for more soon.
Your style is very unique compared to other folks I’ve read stuff from. Thanks for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this web site.
You’re so interesting! I don’t think I have read through a single thing like this before. So wonderful to discover someone with a few unique thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This web site is something that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality.
Saved as a favorite, I love your blog.
The next time I read a blog, I hope that it won’t disappoint me just as much as this particular one. After all, Yes, it was my choice to read, nonetheless I genuinely believed you’d have something helpful to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of crying about something that you could fix if you were not too busy searching for attention.
Right here is the right blog for everyone who wishes to find out about this topic. You understand a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want to…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic that has been written about for decades. Wonderful stuff, just wonderful.
I blog frequently and I truly thank you for your information. The article has really peaked my interest. I am going to bookmark your blog and keep checking for new information about once per week. I subscribed to your RSS feed too.
Oh my goodness! Impressive article dude! Thanks, However I am encountering troubles with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I cannot subscribe to it. Is there anyone else having the same RSS problems? Anyone that knows the solution will you kindly respond? Thanx!!
I would like to thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this website. I’m hoping to view the same high-grade content from you later on as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own site now 😉
The valuation of your investment would not see a downward curve unless there is a pure calamity.
Bourges, below The Duke Jean du Berry, the brother of King Charles V of France, was a significant heart for stained glass in the fifteenth century.
I couldn’t resist commenting. Perfectly written.
If potential, get a letter from the council stating all constructing necessities have been met in any other case this will need to be finished after the transfer in which can imply extra prices and delays.
Good post! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Oh my goodness! Impressive article dude! Many thanks, However I am encountering difficulties with your RSS. I don’t understand why I am unable to join it. Is there anyone else having similar RSS issues? Anyone who knows the answer will you kindly respond? Thanx!
You’ve made some really good points there. I looked on the net for additional information about the issue and found most individuals will go along with your views on this website.
This excellent website definitely has all the information and facts I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
In the everyday case such financial savings are gained by way of analysis and plannning, so that organizations handle their initiatives and operations in a way that takes the very best benefit of the taxation laws and rules.
I love reading through an article that can make people think. Also, many thanks for permitting me to comment.
A motivating discussion is definitely worth comment. I do believe that you should publish more about this issue, it may not be a taboo matter but generally people don’t speak about such topics. To the next! Best wishes.
When I initially commented I appear to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on whenever a comment is added I receive four emails with the exact same comment. There has to be a means you can remove me from that service? Appreciate it.
An intriguing discussion may be valued at comment. I think that you ought to write more about this topic, may possibly not become a taboo subject but normally persons are insufficient to chat on such topics. An additional. Cheers
i would always love to hear those christmas music with a very happy tune’
When I view your RSS feed it puts up a bunch of garbage, is the issue on my end?
Aw, this was a very nice post. Finding the time and actual effort to create a top notch article… but what can I say… I procrastinate a lot and don’t seem to get nearly anything done.
May I simply say what a relief to discover a person that truly understands what they’re talking about on the net. You definitely realize how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people ought to read this and understand this side of your story. I was surprised that you aren’t more popular since you most certainly have the gift.
Ding had been unable to play all through a lot of the COVID-19 pandemic, nevertheless, and had to play a number of hastily arranged matches to reach the minimum FIDE activity requirements to safe his place in the tournament.
Another excellent post on running a blog! Many thanks therefore considerably for taking time to talk about you information as well as knowledge with other writers.
Great post. I will be facing a few of these issues as well..
I blog frequently and I genuinely appreciate your information. This article has truly peaked my interest. I will take a note of your blog and keep checking for new details about once a week. I opted in for your RSS feed as well.
Chevelles offered in California couldn’t get the 307 V-8 but carried a 350-cubic-inch engine as an alternative.
There are a few intriguing points on time in this post but I don’t know if them all center to heart. There may be some validity but I’m going to take hold opinion until I take a look at it further. Very good write-up , thanks and we want more! Added to FeedBurner in addition
fantastic points altogether, you just won brand new reader. What might you recommend about your post that you simply made a few days ago? Any positive?
I needed to thank you for this great read!! I definitely enjoyed every bit of it. I have you book-marked to look at new things you post…
my kids really like to play with those assorted pool toys, they specially like pokemon pool toys and stuff like that..
Howdy! This post couldn’t be written any better! Going through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He constantly kept talking about this. I am going to send this post to him. Pretty sure he will have a very good read. Many thanks for sharing!
Wohh precisely what I was looking for, thanks for putting up. “Be nice to everyone on your way to the top because you pass them all on the way down.” by Fred Hufnagel, Sr..
When I originally left a comment I appear to have clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on whenever a comment is added I receive 4 emails with the same comment. There has to be a way you are able to remove me from that service? Thank you.
Everything is very open with a precise description of the challenges. It was really informative. Your site is extremely helpful. Many thanks for sharing!
Very nice article. I certainly appreciate this website. Keep writing!
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is an extremely well written article. I will be sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post. I’ll certainly comeback.
After I initially commented I seem to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now whenever a comment is added I get 4 emails with the exact same comment. There has to be an easy method you can remove me from that service? Thanks.
Everything is very open with a precise explanation of the challenges. It was truly informative. Your website is extremely helpful. Thanks for sharing!
I really love your blog.. Excellent colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Please reply back as I’m attempting to create my own personal website and would like to learn where you got this from or just what the theme is called. Appreciate it.
Very good write-up. I certainly love this site. Keep it up!
The Christian Council of Tours of 567 established Advent because the season of preparation for Christmas, as well because the season of Christmastide, declaring “the twelve days between Christmas and Epiphany to be one unified festal cycle”, thus giving significance both to 25 December and to 6 January, an answer that will “coordinate the photo voltaic Julian calendar with the lunar calendars of its provinces within the east”.
Very good info. Lucky me I ran across your website by accident (stumbleupon). I have saved as a favorite for later!
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you writing this article and also the rest of the website is also really good.
After I originally left a comment I appear to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on every time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. There has to be a means you can remove me from that service? Thanks.
Aw, this was an incredibly nice post. Spending some time and actual effort to produce a good article… but what can I say… I put things off a lot and never manage to get nearly anything done.
This is the perfect site for everyone who really wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want to…HaHa). You definitely put a fresh spin on a subject that’s been written about for years. Excellent stuff, just wonderful.
After going over a few of the articles on your blog, I seriously like your technique of blogging. I added it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Please visit my website as well and tell me your opinion.
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Many thanks, However I am experiencing difficulties with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I cannot subscribe to it. Is there anybody else having similar RSS problems? Anyone who knows the answer will you kindly respond? Thanks!!
I was excited to discover this great site. I wanted to thank you for ones time for this particularly fantastic read!! I definitely appreciated every little bit of it and I have you book marked to look at new information on your website.
Very good post! We are linking to this great post on our site. Keep up the great writing.
Pretty! This was an extremely wonderful article. Thanks for providing this information.
I really love your website.. Pleasant colors & theme. Did you build this amazing site yourself? Please reply back as I’m planning to create my very own site and want to learn where you got this from or what the theme is called. Kudos.
This site was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve found something that helped me. Thanks!
I have to express some appreciation to the writer just for rescuing me from this type of dilemma. Just after looking out through the search engines and obtaining techniques that were not pleasant, I believed my life was over. Existing without the presence of answers to the issues you’ve sorted out through your entire guideline is a crucial case, as well as those which could have in a wrong way damaged my career if I hadn’t come across the website. The talents and kindness in touching all the details was very helpful. I don’t know what I would have done if I had not encountered such a point like this. I can at this point look ahead to my future. Thank you very much for the high quality and results-oriented help. I won’t be reluctant to recommend your site to anyone who needs guidelines about this matter.
Although it’s a favourite alcoholic beverage right this moment, the invention of fermented barley was so monumental that the Mesopotamians instantly wrote down the recipe and named a god after it.
It is an ideal website.
On 12 March 2011, with common goalkeeper Tobias Sippel sidelined with influenza, he made his Bundesliga debut in a 2-1 home win over SC Freiburg.
Karpov resigned on move 42, his rook is no match for White’s queen.
I’m curious to find out what blog platform you are using? I’m experiencing some minor security issues with my latest site and I’d like to find something more secure. Do you have any solutions?
I am not sure where you are getting your information, but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more. Thanks for excellent information I was looking for this information for my mission.
Sometimes, an trustworthy reply seems like a social gaffe.
I dugg some of you post as I cerebrated they were very beneficial very useful
you have got a great blog right here! would you like to make some invite posts on my weblog?
Thanks for the points you have provided here. Yet another thing I would like to say is that personal computer memory demands generally rise along with other advances in the technologies. For instance, whenever new generations of cpus are introduced to the market, there is usually a corresponding increase in the size calls for of both the computer system memory plus hard drive room. This is because software program operated simply by these processor chips will inevitably boost in power to benefit from the new know-how.
Hi there! Would you make use of Facebook? My partner and i’d like to adhere to you in the event it would be alright. My partner and i’m totally enjoying your website and appear to brand new revisions.
maintaining a healthy weight can be tricky because it revolves around genetics and some other factors*
prom dresses that are bright colored like rose red are the best for a girl,`
Hi there! This article could not be written much better! Looking through this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He always kept preaching about this. I’ll forward this information to him. Pretty sure he’ll have a great read. Thank you for sharing!
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know so much about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with some pics to drive the message home a little bit, but other than that, this is fantastic blog. An excellent read. I’ll definitely be back.
You ought to actually think about engaged on creating this blog into a significant authority on this market. You evidently have a grasp handle of the topics everyone seems to be trying to find on this website in any case and you could actually even earn a buck or two off of some advertisements. Id discover following latest subjects and raising the quantity of write ups you place up and I guarantee you’d begin seeing some amazing targeted traffic within the close to future. Only a thought, good luck in no matter you do!
Can I just now say what a relief to uncover someone who actually knows what theyre preaching about over the internet. You actually realize how to bring a concern to light and produce it critical. More and more people need to ought to see this and understand this side from the story. I cant believe youre less well-liked when you definitely provide the gift.
You really make it appear so easy along with your presentation but I in finding this topic to be actually something that I believe I might by no means understand. It seems too complicated and extremely huge for me. I am taking a look forward to your subsequent submit, I will try to get the hold of it!
Terrific paintings! This is the kind of info that are meant to be shared across the internet. Disgrace on the seek for not positioning this submit upper! Come on over and seek advice from my site . Thanks =)
Et bien oui et aussi pas vraiment. Certes parce que il est probable qu’on acquiert certaines sources qui certainement accusent les memes validités. Non puisque il ne suffit pas de reproduire ce que l’on a la possibilité de retouver sur des articles autres et le transposer tellement clairement;
Hi are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and create my own. Do you need any coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
I don’t even know how I returned, however i presumed this kind of submit has been practical. Cheers!
I’ve recently started a site, the information you offer on this web site has helped me greatly. Thank you for all of your time & work.
What’s the very best steakhouse in Cave Creek?
I would really like you to become a guest poster on my blog..”.;
I keep listening to the news bulletin lecture about receiving free online grant applications so I have been looking around for the most excellent site to get one. Could you advise me please, where could i get some?
very good put up, i certainly love this website, carry on it
I’m impressed, I have to admit. Really rarely do you encounter a weblog that’s both educative and entertaining, and without a doubt, you might have hit the nail to the head. Your idea is outstanding; the problem is an element that not enough individuals are speaking intelligently about. My business is very happy that we stumbled across this within my look for something relating to this.
I am glad that I noticed this web blog, precisely the right info that I was looking for!
An interesting discussion might be priced at comment. I do think that you should write more about this topic, it might not become a taboo subject but normally everyone is too few to talk on such topics. Yet another. Cheers
My friend first found your blog on Google and she referred your blog to me.,”..’
This is a topic that’s near to my heart… Cheers! Where can I find the contact details for questions?
Just right points?I would observe that as any individual who actually doesn’t write on blogs a lot (if truth be told, this can be my first post), I don’t think the term ‘lurker’ may be very becoming to a non-posting reader. It’s now not your fault in the least , however possibly the blogosphere could come up with a better, non-creepy identify for the ninety people that revel in reading the content .
pretty valuable material, overall I imagine this is really worth a bookmark, thanks
Simply wanna remark that you have a very decent internet site , I love the style it actually stands out.
Great looking web site. Precisely what theme are you presently making use of?
Aw, it was an extremely good post. In concept I would like to invest writing this way moreover – spending time and actual effort to make a top notch article… but exactly what can I say… I procrastinate alot by no indicates find a way to get something accomplished.
An fascinating discussion will probably be worth comment. I do believe that you simply write on this topic, may well often be a taboo subject but usually individuals are there are not enough to communicate on such topics. To another location. Cheers
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Looking at this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He constantly kept talking about this. I most certainly will forward this post to him. Pretty sure he will have a very good read. Thanks for sharing!
The biggest issue is the dialogue, it is a little cheesy at times and doesn’t give the actors much to work with, but I wouldn’t say it’s every time they open their mouth just some lines in the movie are a little rough.
Your home is valueble for me. Thanks!? This web page is really a walk-via for all of the information you needed about this and didn know who to ask. Glimpse right here, and you l definitely uncover it.
Your current posts usually possess a decent amount of really up to date info. Where do you come up with this? Just stating you are very imaginative. Thanks again
Awesome read. I just passed this onto a buddy who was doing a little research on that. He just bought me lunch because I found it for him! Thus let me rephrase: Thanx for lunch!
You produced some decent points there. I looked online for that issue and found most people will go coupled with with all your website.
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive read anything similar to this prior to. So nice to locate somebody with a few original applying for grants this subject. realy thanks for starting this up. this fabulous website are some things that is needed online, an individual with a bit of originality. beneficial project for bringing something new to the net!
I don’t think I’ve read a post like this before. It’s well-thought out, which means that I learned something new today. I’m going to check out some of your other posts to see if they each have the same high-quality applied to them!
It’s nearly impossible to find knowledgeable people about this subject, however, you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
After study few of the articles on your blog nowadays, and that i like your approach of blogging. I tag it to my favorites net site list and can be checking back soon. Please visit my web site too and let me grasp your thought.
Slide small cooking pot in the cable to make it easier for you to link the other big wooden bead for the conclude with the cord.
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon everyday. It’s always helpful to read content from other writers and use a little something from their websites.
certainly like your web-site but you have to check the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I in finding it very bothersome to inform the truth however I will definitely come again again.
Native American inhabitants is markedly higher (11.7 vs.
Well-identified decorators like Sister Parrish had integrated nation items into their designs for years, however now everyone was on the bandwagon.
Afterward, they took a protracted horseback trek to Kentucky, left their ladies and traveled all the way down to the Cumberland Settlements in late 1778, building a station on the southern aspect of the Cumberland River above the French Lick, on the excessive floor where Nashville now stands, within the early spring of 1779.
Mandarake is a chain of outlets that specialize in buying and selling second-hand collectible toys and hobby objects.
Darth Atrius – Historical Darkish Lord of the Sith who lived before Darth Bane and the trendy Sith.
Having read this I believed it was really enlightening. I appreciate you spending some time and effort to put this informative article together. I once again find myself personally spending a significant amount of time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worth it.
Plus, I get some alone time in the kitchen.
You are so interesting! I do not believe I have read through something like that before. So nice to discover someone with unique thoughts on this topic. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is needed on the web, someone with some originality.
I really like reading through a post that will make men and women think. Also, thanks for permitting me to comment.
Hi, I do think this is a great website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m going to return yet again since I saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.
Greetings, I think your site could possibly be having web browser compatibility issues. When I look at your web site in Safari, it looks fine however when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping issues. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Aside from that, fantastic blog!
I couldn’t resist commenting. Well written.
When the sport first obtained its begin within the 1980s, beefing up the engines meant adding turbochargers — the larger the higher.
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with SEO?
I’m trying to get my site to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good gains.
If you know of any please share. Kudos! You can read similar art here:
Bij nl
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.